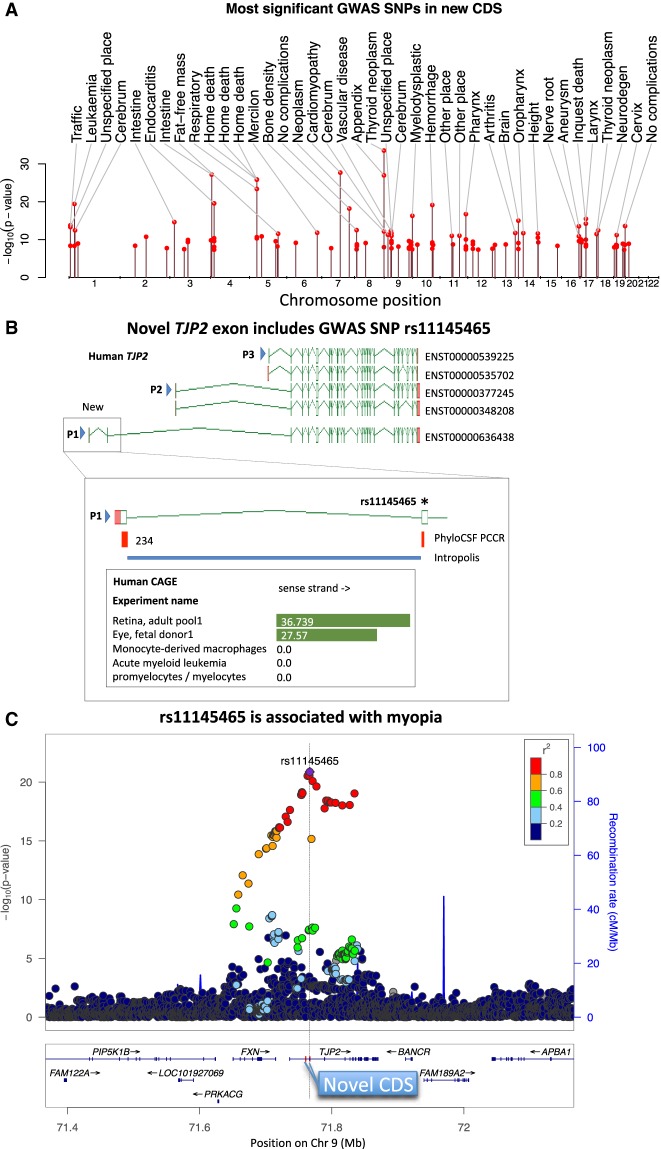
Figure 3.
Protein-altering disease variants. (A) Chromosomal positions and strength of association for the 118 SNVs in newly annotated CDSs that were previously found to be significantly associated with diseases or other traits, with the trait abbreviation from Supplemental Data S5 listed for the 40 most significant associations. (B) Novel coding sequence added to human TJP2 locus includes an eye disease–associated variant. Previous GENCODE annotation represented by models ENST00000539225, ENST00000535702, ENST00000377245, and ENST00000348208. Additional transcriptional complexity omitted for clarity. PhyloCSF PCCRs indicated the presence of two additional coding exons (dotted box and inset) that led to annotation of novel coding transcript model ENST00000636438, which lacks cDNA or EST support but whose intron is confidently supported by short read data in Intropolis (blue rectangle) mostly from a retinal study (Farkas et al. 2013), and whose TSS (P1) is supported by FANTOM5 CAGE data, limited to retina and eye (data from ZENBU browser, precisely redrawn for clarity; scores represent sequence read counts, with zeros for the next three experiments included for comparison). In contrast, TSSs P2 and P3 have negligible CAGE support for eye expression, with profiles dominated by monocyte and central nervous system expression. FANTOM5 CAGE also shows eye-specific expression for an equivalent mouse model added as part of this study, also supported by eye-experiment ESTs (e.g., BU505208.1). The second coding exon added to human GENCODE contains GWAS variant rs11145465, identified in a study of refractive error and myopia with a P-value of 7 × 10−9 (Verhoeven et al. 2013). In that study, the variant had been interpreted as noncoding based on RefSeq annotation, but it can now be reclassified as a missense mutation of an amino acid that is perfectly conserved in the mammal and avian clades. (C) Regional association plot for eye disease. All SNPs in an 800-kb window with their strength of association with refractive error and myopia in a more recent study (Tedja et al. 2018) show that rs11145465 has the strongest association. The positions of the novel coding exons of ENST00000636438 have been added in red.