Figure 2.
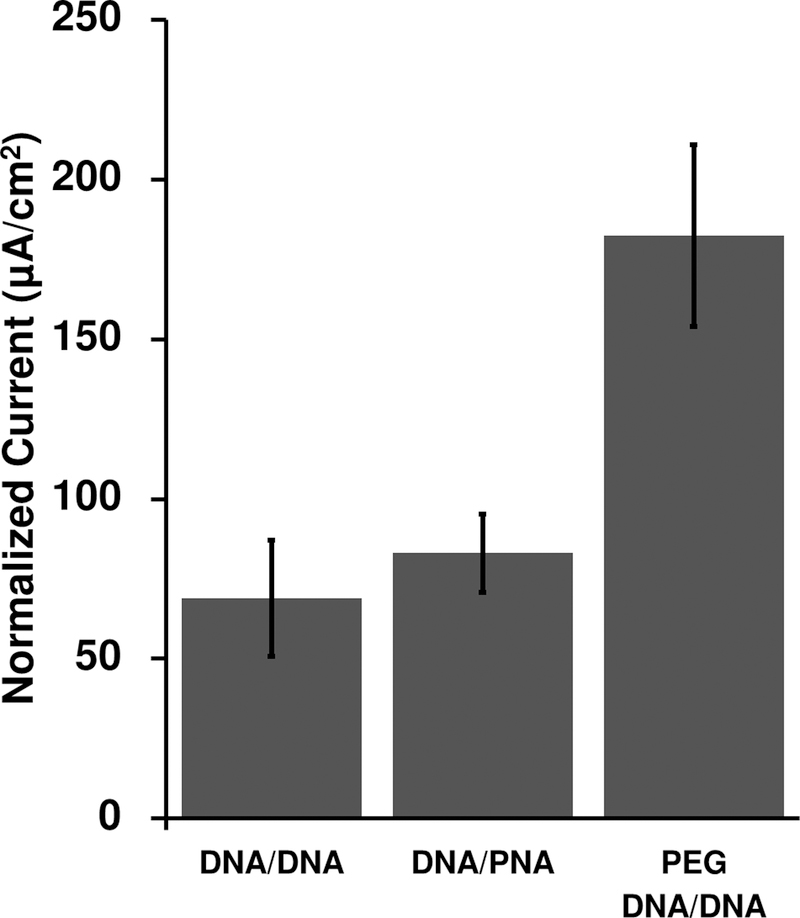
Here we compare the signaling of three sensor architectures varying in scaffold flexibility: a fully-double-stranded DNA scaffold (DNA/DNA), a DNA/peptide-nucleic-acid (PNA) scaffold, and a double stranded scaffold connected to the surface via a flexible polyethylene glycol (PEG) linker. The PEG DNA/DNA scaffold provides approximately twice the current (for a given sized sensor) as our previously employed, DNA/DNA scaffold, and thus we have employed it here. For each construct, we measured the peak current of nine individually fabricated electrodes and normalized each by the surface area of the individual electrode.