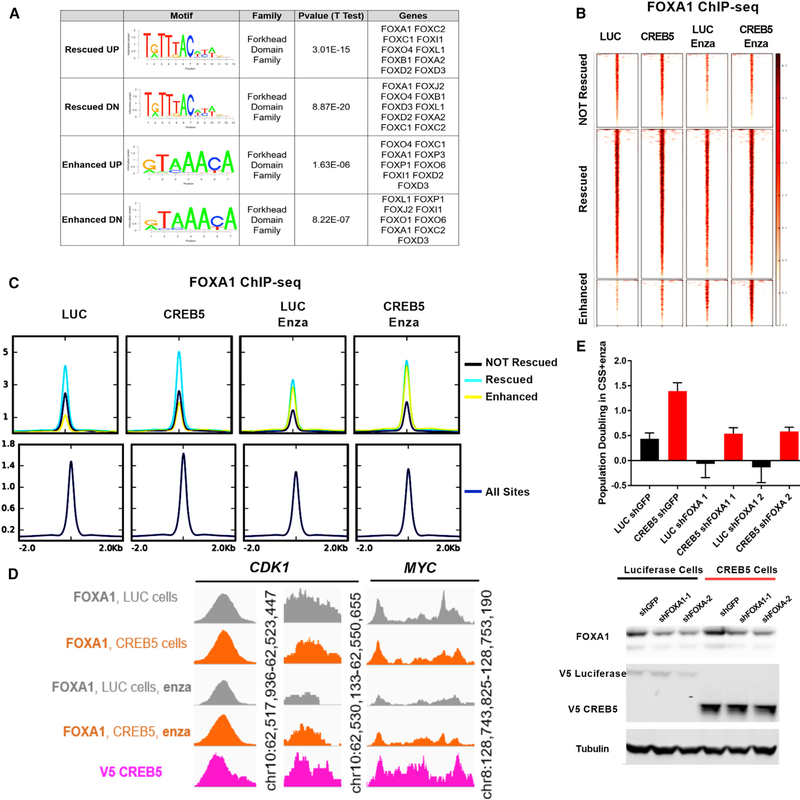
Figure 5. FOXA1 Is Necessary for CREB5-Mediated Enzalutamide Resistance.
(A) Motif enrichment analysis was performed on AR/CREB5-co-bound sequences.
(B) FOXA1 ChIP-seq demonstrated FOXA1 binding at the 11,484 CREB5/AR binding sites in luciferase control or CREB5-overexpressing cells with or without enzalutamide treatment.
(C) FOXA1 binding sites are categorized based on CREB5/AR not rescued (black), rescued (teal), and enhanced (yellow). The integrated binding signal is shown relative to all FOXA1 binding sites (navy).
(D) FOXA1 interactions at binding sites upstream of CDK1 and MYC.
(E) The relative proliferation of cells in CSS + enzalutamide without pre-treatment. FOXA1 was suppressed using two shRNAs in either CREB5-overexpressing (red) or luciferase-overexpressing (black) LNCaP cells. The mean ± SD of three replicates is shown. Immunoblots depict the levels of FOXA1, V5-luciferase, and V5-CREB5. Tubulin is used as a loading control.