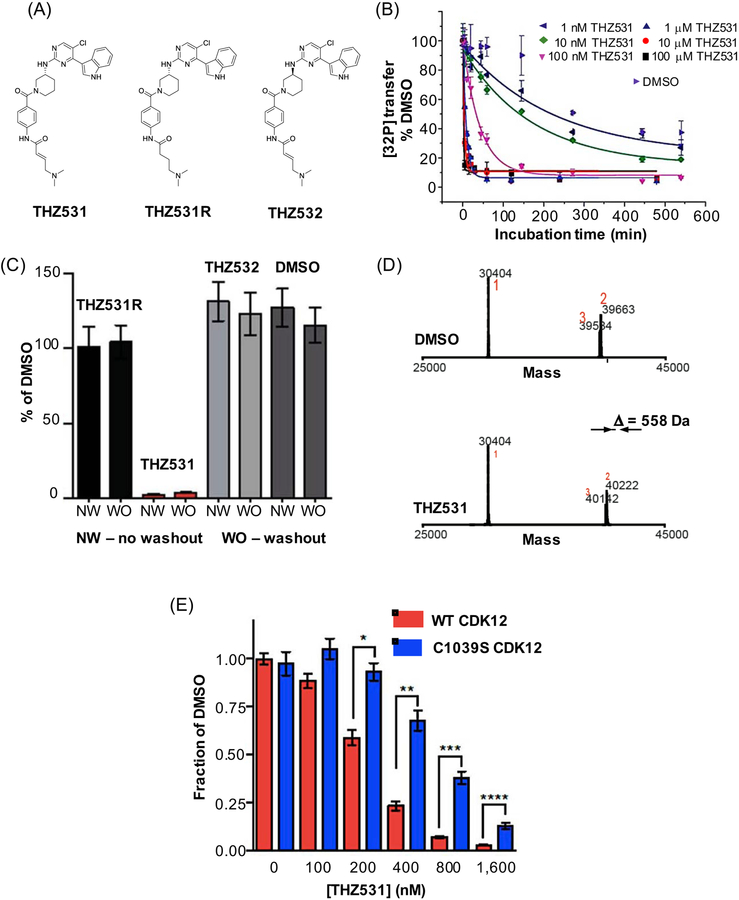
Figure 2. Validating THZ531, a CDK12/13 irreversible covalent inhibitor.
(A) chemical structures of THZ531, a CDK12/13 inhibitor, and two negative control compounds, an enantiomer THZ532, and a reversible, noncovalent binder THZ531R; (B) preincubation time-dependent in vitro activity is a signature behavior of irreversible covalent inhibitors. In this experiment in vitro kinase activity assay of CDK12-cyclin K was measured using different concentrations of THZ531 (1 nM to 100 μM) and varying preincubation times and expressed as relative [32P] transfer; (C) irreversible covalent inhibitors retain activity in cell-based assays upon washout as shown for THZ531 and two negative control compounds, THZ531R and THZ532. Jurkat cells were treated with the indicated compounds for 6 hrs, inhibitor was washed out and cells were allowed to grow for the remainder of the 72 hr (washout, WO). This growth was compared to the growth of cells treated with inhibitors for the full 72 hrs (no washout, NW); (D) intact mass spectrometry (MS) offers evidence for covalent adduct formation based on mass difference between DMSO treated and THZ531 treated CDK12. 558 Da difference observed here corresponds to Cys-directed THZ531 adduct; and (E) 72-hour antiproliferation assay using WT and Cys1039Ser cells and different concentrations of THZ531. Under all concentrations tested, mutant cell lines display resistance to THZ531, highlighting that Cys1039 is important for mediating THZ531 effects. Panels (B), (C), (D) and (F) have been reproduced and/or modified from Zhang et al., 2016 with premission, Copyright 2016, Springer Nature.