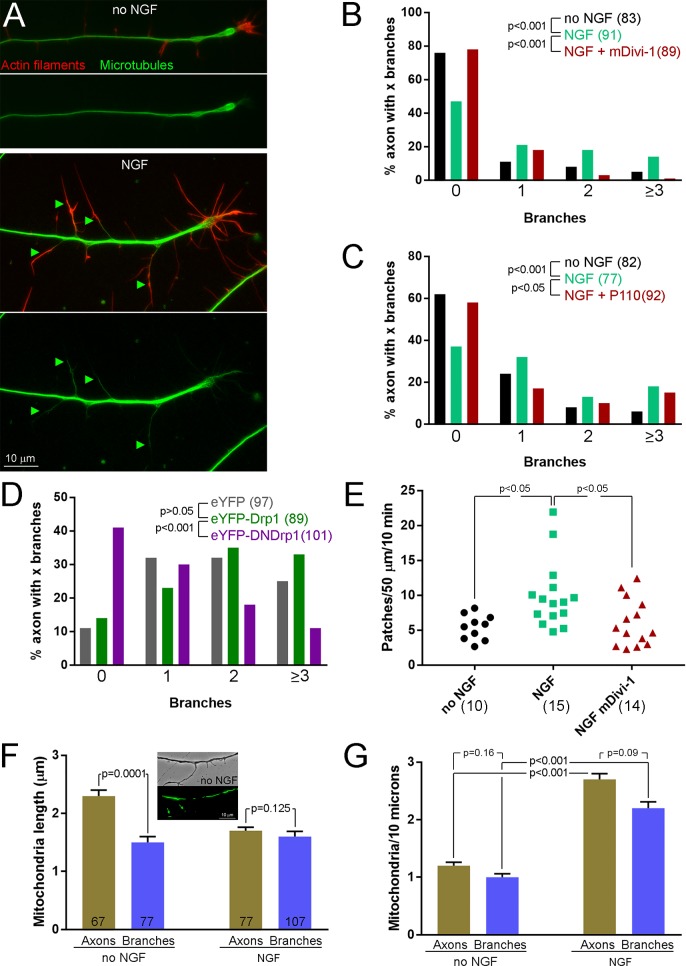
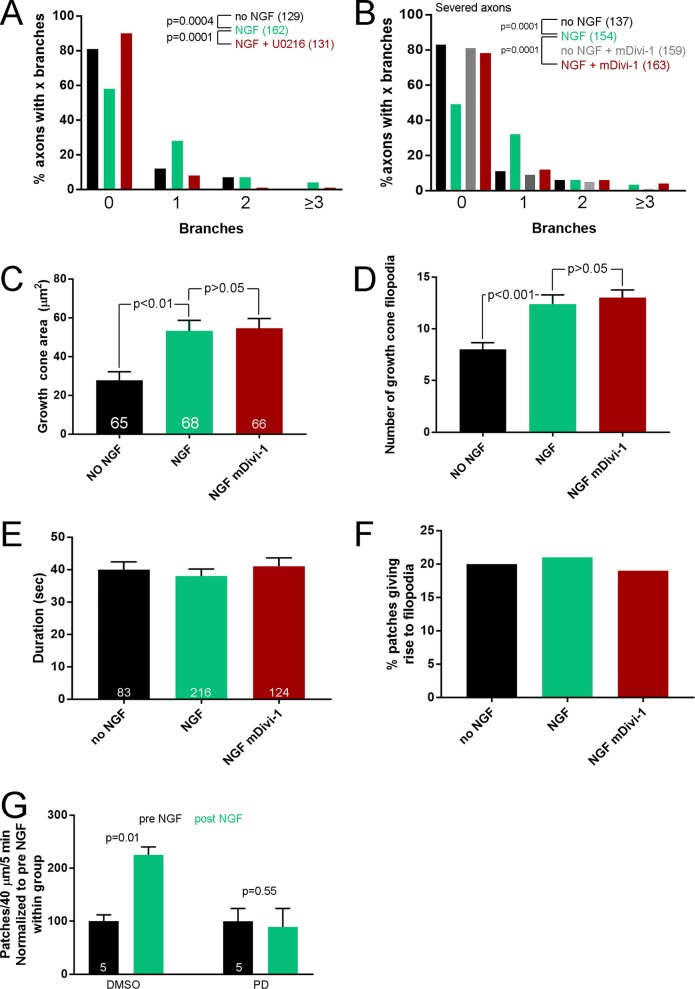
Figure 5. Inhibition of fission impairs NGF-induced axon branching.
(A) Example of NGF-induced axon branching. Top panels show axonal morphology in the no NGF treatment group. Some axonal filopodia are present but not branches. Bottom panels show an NGF-treated axons with four branches (green arrowheads). Mature branches contain microtubules and distally actin filaments. (B) Quantification of axon branches ± mDivi-1 or DMSO pretreatment. For panels (B)-(D) n = axon numbers shown in (). Mann-Whitney test. (C) Quantification of axon branches ± P110 or vehicle pretreatment. Mann-Whitney test. (D) Quantification of axon branches in dissociated neurons cultured overnight in NGF expressing eYFP (baseline control), eYFP-Drp1 or eYFP-DNDrp1. The differences in baseline branch number reflect the use of dissociated neurons relative to explant cultures as in panels (B) and (C) for the acute NGF treatment experiments. Mann-Whitney test. (E) Quantification of the rates of actin patch formation ±mDivi-1 or DMSO treatment. Each data point reflects one axon and the number of axons is shown in () below the data. Dunn’s posthoc multiple comparison tests. (F) and (G) Quantification of mitochondria length and density, respectively, in the axons and branches of axons emanating from explants raised in either no NGF or NGF overnight. n = axons shown in the bars labeled Axons; n for branches from this set of axons is denoted in the bars labeled Branches. Mean and SEM. Mann-Whitney tests.