Fig. 1.
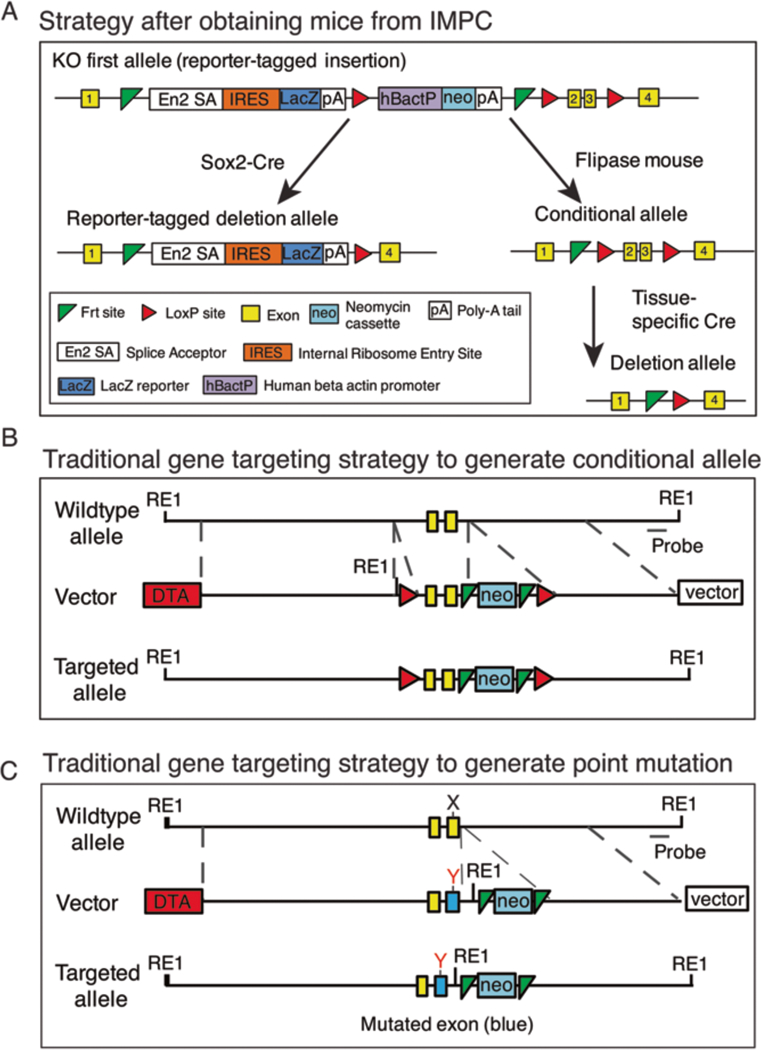
Mouse generation strategies. (A) Mice obtained from the International Mouse Phenotype Consortium (IMPC) can be crossed with Sox2-Cre mice to generate global knockout mice. Alternatively, they can be crossed with flippase deleter mice to generate the conditional allele followed by a tissue-specific Cre deletion in the relevant tissue or cell type. (B) The traditional gene targeting approach inserts two 34 base pair sequences referred to as loxP sites (red triangles) that flank either side of a critical exon in a gene of interest and a neomycin cassette for embryonic stem (ES) cell selection. Diptheria toxin A gene is incorporated outside of the homology arms to select against ES colonies that have not taken up the insert by homologous recombination. A new restriction enzyme site is introduced in the mutant construct to aid screening with Southern blotting. (C) Traditional gene targeting approach to generate the substitution mutation from nucleotide X to Y in an exon (blue)
