Fig. 2.
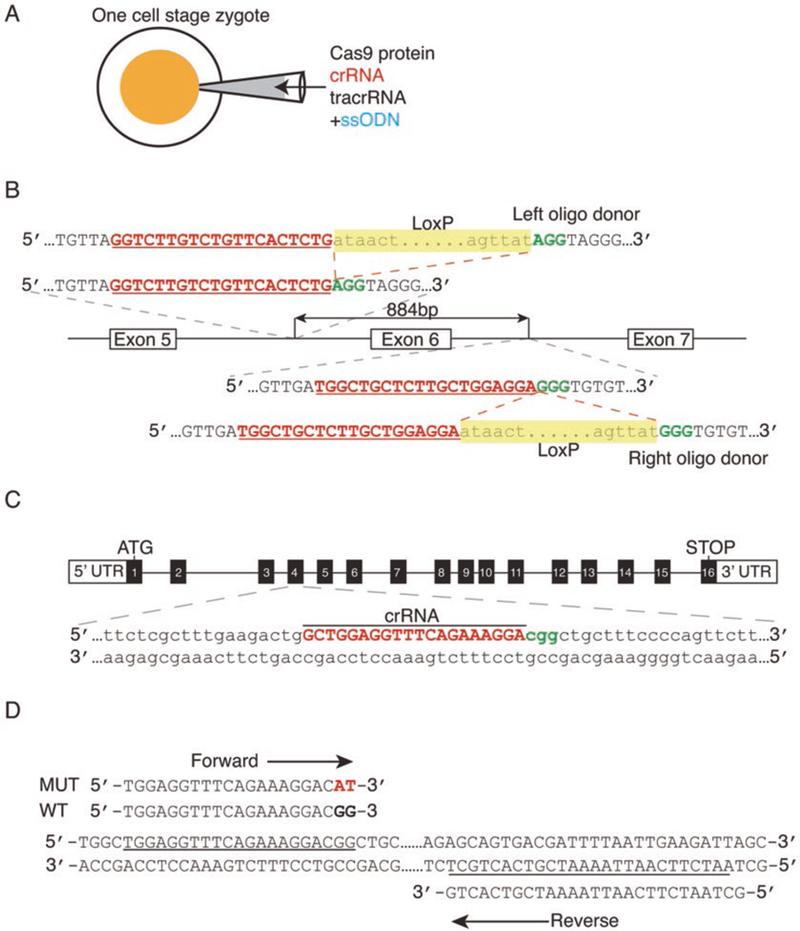
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene manipulation to generate floxed and point mutation alleles. (A) A cloning-free CRISPR/Cas9 system by pronuclear injection into a one-cell stage zygote of commercial Cas9 protein combined with chemically synthesized CRISPR RNA (crRNA), trans-activating crRNA (tracrRNA), and single-strand oligodeoxynucleotides (ssODNs). (B) Schematic illustration to generate a conditional allele by insertion of two loxP sites. In this method, two crRNAs are designed to direct the Cas9 to target the upstream and downstream introns of the target exon, along with corresponding loxP site oligos with 60 bp homology sequences on either side surrounding each Cas9-mediated double-strand break. The protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) is shown in green. In the oligo donor sequence, the loxP site is highlighted in yellow. (C) To generate point mutation mice, the sequence of the crRNA (red) targets the Cas9 nuclease to the desired mutation-specific region (in this example, CGG to CAT) of the target gene. The PAM is shown in green. (D) Design of the mutation-specific primers with a site-specific variant sequence at the 3’ terminus of the forward primer to screen for correctly targeted mice. Figure modified from [9]
