Figure 7.
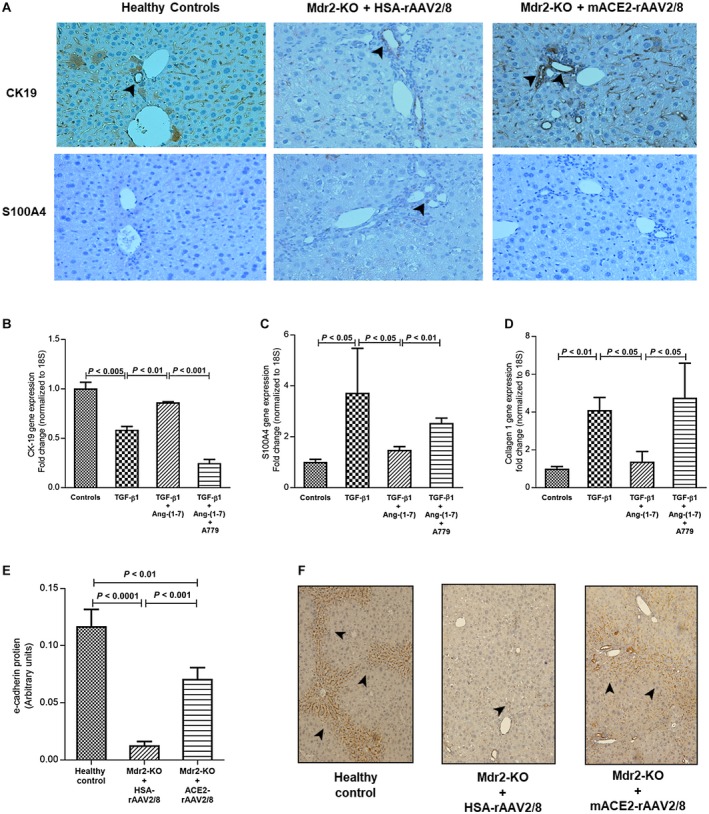
Effect of ACE2 treatment on protein expression of epithelial (CK‐19) and mesenchymal (S100A4) markers; effect of Ang‐(1‐7) on gene expression of CK‐19, S100A4, and collagen 1 in TGF‐β1‐activated cholangiocytes (H69 cells); and effect of ACE2 treatment on e‐cadherin protein in Mdr2‐KO mice. (A) ACE2 therapy restored epithelial characteristics of cholangiocytes, as reflected by increased CK‐19 expression, and prevented transdifferentiation into a mesenchymal phenotype, as reflected by reduced S100A4 expression in Mdr2‐KO mice. In support of the inhibition of EMT of cholangiocytes by ACE2‐derived Ang‐(1‐7) in the animal model, Ang‐(1‐7) prevented TGF‐β1‐induced (B) down‐regulation of CK‐19 expression and (C) up‐regulation of S100A4 expression, leading to (D) inhibition of collagen 1 expression. Thus, Ang‐(1‐7) inhibited EMT of cholangiocytes, which was completely blocked by MasR blocker A779. (E,F) Moreover, ACE2 therapy restored protein expression of e‐cadherin (another epithelial marker known to protect from cholangiopathies) in Mdr2‐KO mice. (A,F) Arrowhead shows positive staining (magnification ×200). Each bar in (B‐D) represents the mean ± SEM profile from three independent experiments. Each bar in (E) represents the mean ± SEM profile from n = 12‐15 mice per treatment group.
