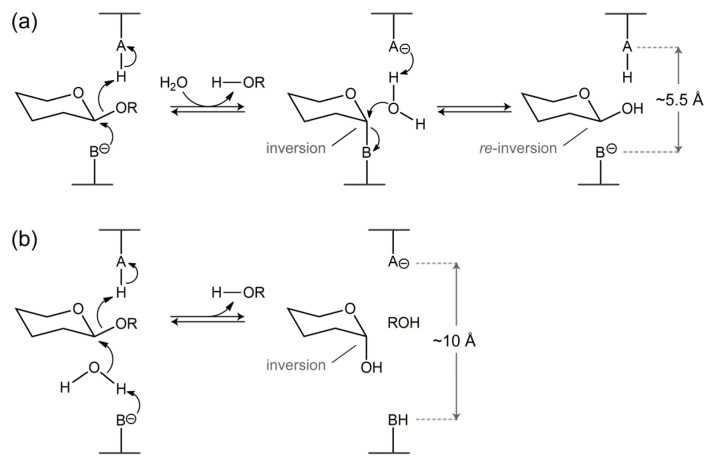
Figure 5.
The two common types of catalysis by glycoside hydrolases as adapted from Davies and Henrissat [29]. (a) The retaining mechanism. The nucleophile and the general acid/base are represented as B- and AH, respectively. (b) The inverting mechanism. The general base and the general acid are represented as B- and AH, respectively. The typical distances of the catalytic residues in both mechanisms are indicated in Å. In most GHs, A and B are either Asp or Glu. See main text for further details.