Figure 2.
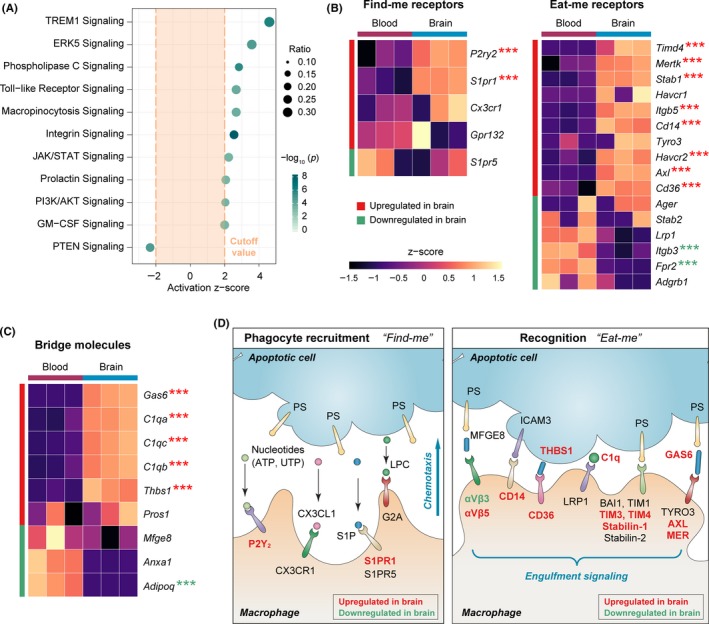
Poststroke brain macrophages upregulate genes participating in the recognition of apoptotic cells during efferocytosis. A, IPA was performed on the DEGs in monocytes/macrophages from post‐dMCAO brain versus blood. Shown are the phagocytosis‐related canonical signaling pathways predicted to be significantly activated (z‐score >2, P < .01) or inhibited (z‐score <−2, P < .01) in brain macrophages. B, Heatmaps of the expression profiles of receptors involved in the “find‐me” (left panel) and “eat‐me” (right panel) steps of macrophage efferocytosis. C, Heatmap of the expression profiles of bridge molecules that assist with the recognition of apoptotic cells during macrophage efferocytosis. Each row represents one gene, and each column represents one sample. Color represents the scaled expression value (row z‐score). Genes that were significantly upregulated or downregulated in brain macrophages were labeled by asterisks, where *** indicates an adjusted P‐value <.001. D, The DEGs in B and C were manually annotated according to their functional roles in the phagocyte recruitment stage (left panel) and recognition stage (right panel) of efferocytosis. Genes that were significantly upregulated or downregulated in brain macrophages were labeled in red or green, respectively. LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine. PS, phosphatidylserine. S1P, sphingosine‐1‐phosphate
