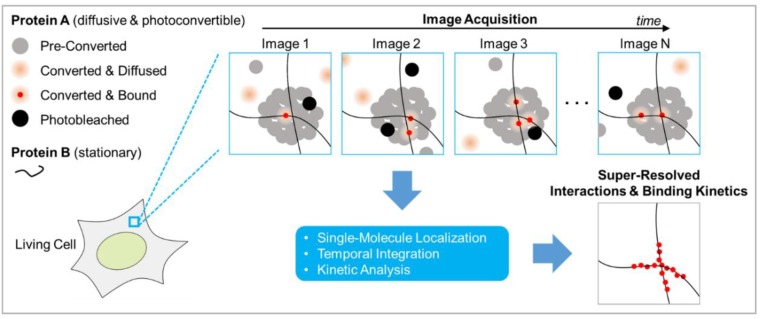
Figure 2.
Principle of super-resolution imaging of biomolecule interactions with PAINT-PALM. For illustration purpose, the interactions between a diffusive protein A and a stationary protein B are shown here. The concept is readily generalizable to the imaging of protein-DNA or protein-RNA interactions in the nucleus, by replacing protein B with DNA or RNA in the figure. Here, the diffusive protein A is fused to a photoconvertible fluorescent protein (FP) and expressed in living cells. During experiment, the chimeric protein A (ligand) is stochastically photoconverted to fluoresces. On camera, the images of unbound protein A molecules appear motion-blurred because of diffusion. The images of protein A molecules interacting with protein B appear as sharp spots with well-defined Gaussian PSF, after transient immobilization. The interactions are sampled over time by acquiring an image sequence (image 1, 2, 3, …, N). Super-resolved interaction map is generated by single-molecule localization and temporal integration. The temporal image sequence may also be subjected to additional analysis such as tcPALM to extract information on binding kinetics.