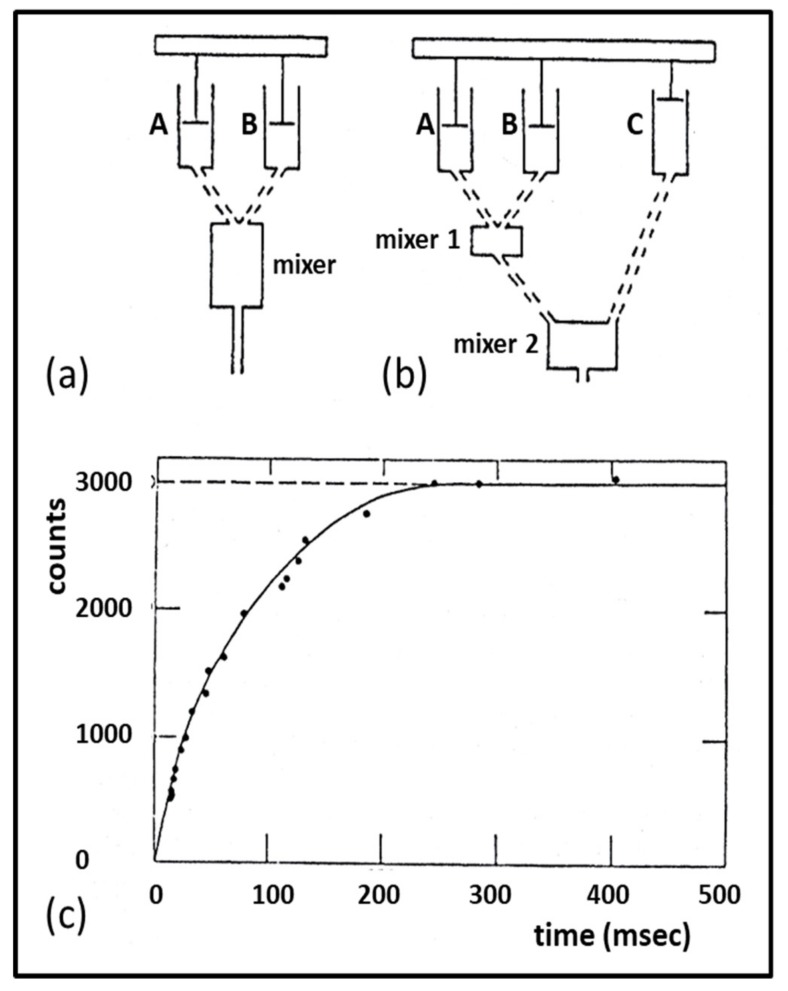
Figure 15.
Apparatus used for rapid reaction kinetics: (a) stopped flow apparatus, (b) quenched flow apparatus. In (a) the reactants are held in syringes A and B and are forced into the mixing chamber C within a few msec. The mixing chamber can be monitored optically to follow the progress of the reaction. In (b) the reactants A and B, as before, are mixed in a small chamber (mixer 1). The flow is continuous, and the reaction proceeds in the tube between mixer 1 and mixer 2, The reaction is quenched in the mixer 2 chamber by the addition of acid from syringe C. (c) Example of a quenched flow result showing phosphate accumulation when rabbit myosin was mixed with Mg-ATP [55]. The initial ATP concentration was 32 M and the magnitude of the Pi burst was 1.2 moles Pi/ mole myosin. (Adapted from [3] after White and Thorson [112]).