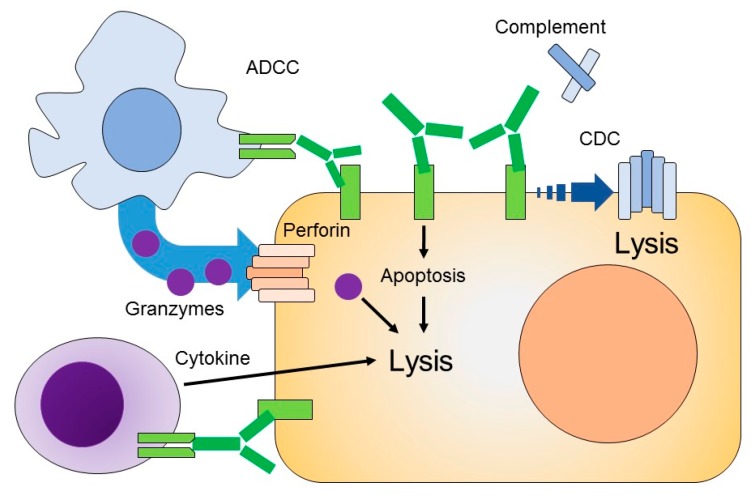
Figure 2.
Mechanism of action of an mAb. The mAb binds to its targeted antigen and provokes antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and a complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) response. ADCC includes (natural killer) NK cells, which release granzymes and cytotoxic agents that are responsible for cell lysis. The Fc region of mAb may also bind to soluble protein C1q to promote a cascade reaction that eventually forms a membrane attack complex, as in the CDC-mediated response. Membrane attack complex (MAC) is responsible for disrupting cell membrane and inducing cell lysis.