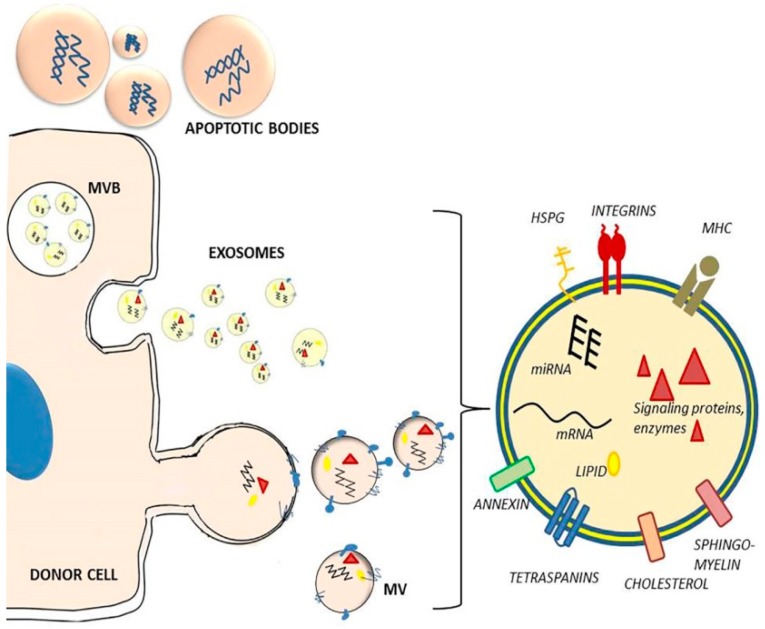
Figure 1.
Types, release, and composition of extracellular vesicles. Based on their generation and size distribution EVs can be divided into exosomes, microvesicles, and apoptotic bodies. Exosomes are formed inside endosomes by inward budding of the membrane, generating multivesicular bodies (MVB). Exosomes are released by fusion of MVB with the plasma membrane. Microvesicles (MV) arise as a result of direct budding and fission of the plasma membrane from the cells. Apoptotic bodies are formed during apoptosis, from outward blebbing of the cell surface. EVs are composed of a phospholipid bilayer with membrane proteins (immuno-regulatory molecules such as MHCI, MHCII, integrins, tetraspanins, receptors, heparan-sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG), annexins, cholesterol, sphingolipids, ceramides), carrying soluble cytosolic components of the donor cell, such as miRNAs, mRNAs, signaling proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, enzymes, and lipids.