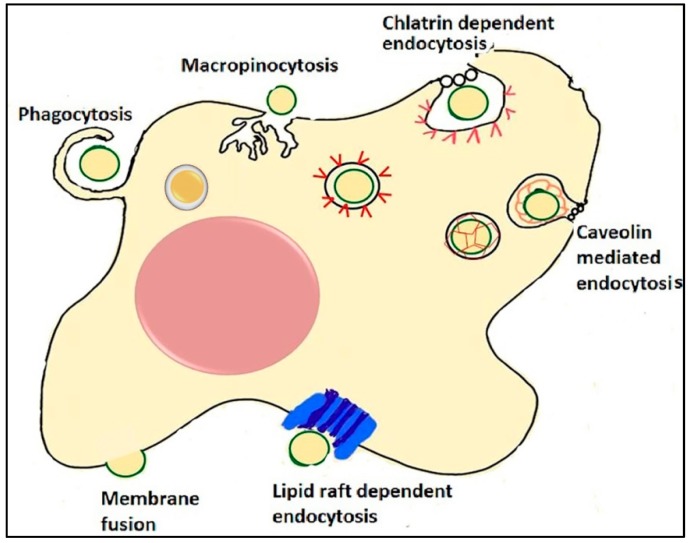
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of EV uptake. EVs can be internalized by cells through different endocytic processes. During phagocytosis, the cytoplasm creates invaginations around the EV, which is then internalized creating an endosome. During macropinocytosis, plasma membrane ruffles fold back on themselves around the EVs, forming a lumen of a macropinosome. Clathrin-dependent endocytosis induces membrane curvature around the EV. In caveolin-mediated endocytosis caveolae (small, cave-like invaginations in the cell membrane) with EVs inside are internalized into the cell. Intracellularly, they develop chlatrin- or caveolin-coated vesicles, fuse with endosomes and deliver the cargo. EV uptake can occur by interaction of EVs with lipid rafts. Lipid rafts are involved in both clathrin- and caveolin-mediated endocytosis. Another possible way for EVs to deliver their cargo to recipient cell is by passive fusion with the plasma membrane.