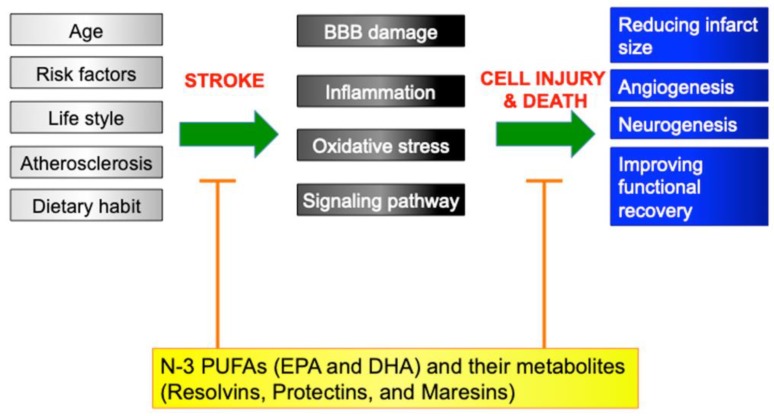
Figure 3.
Scheme of underlying mechanisms before and after stroke. Age, cardiovascular risk factors, atherosclerosis, lifestyle, and dietary habits could be implicated in the mechanisms of stroke development in humans. On the other hand, previous experimental studies showed that the blood–brain barrier (BBB), inflammation, oxidative stress, and pathologic signaling pathways contributed to the mechanisms after stroke. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids including eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and its metabolites, resolvins, protectins, and maresins, suppressed these pathomechanisms, and reduced infarct size, induced angiogenesis and neurogenesis, and improved functional recovery. Bar-headed lines indicate an inhibition, and arrows represent a production and induction.