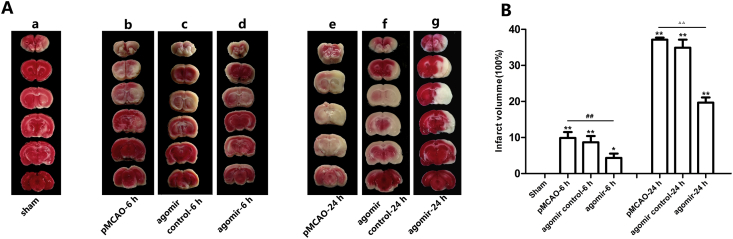
Figure 5.
Representative TTC-stained brain slices showing tissue infarction, which is shown as a white region. No appreciable TTC staining defects were observed in the sham rat brains (a). After 6 h of ischemia, TTC staining defects were clearly identified in the cortex and dorsolateral striatum (b, c, d), and the white region was slightly reduced in the rno-miR-124-3p agomir + pMCAO-6 h group (d). After 24 h of ischemia, the white regions extended to most of the middle cerebral artery supplied territory and went more deeply (e, f, g). Compared to the pMCAO-6 h group (e), the infarct regions were significantly decreased in the pMCAO-6 h + rno-miR-124-3p agomir group (g). Similarly, the infarct regions were significantly decreased in the pMCAO-24 h + rno-miR-124-3p agomir group (g), comparing with the pMCAO-24 h group (e). (a: sham group; b: pMCAO-6 h group; c: rno-miR-124-3p agomir control + pMCAO-6 h group; d: rno-miR-124-3p agomir + pMCAO-6 h group; e: pMCAO-24 h group; f: rno-miR-124-3p agomir control + pMCAO-24 h group; g: rno-miR-124-3p agomir + pMCAO-24 h group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, vs. sham group; ##p < 0.01 vs. pMCAO-6 h group; △△p < 0.01 vs. pMCAO-24 h group. n = 3 in each group).