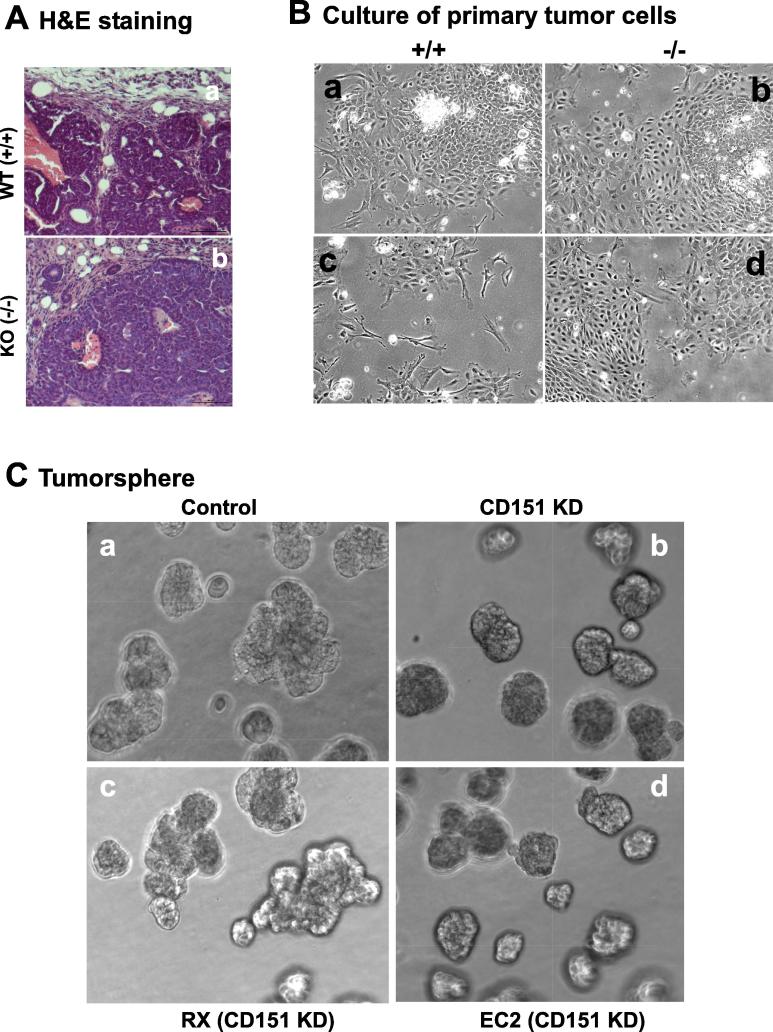
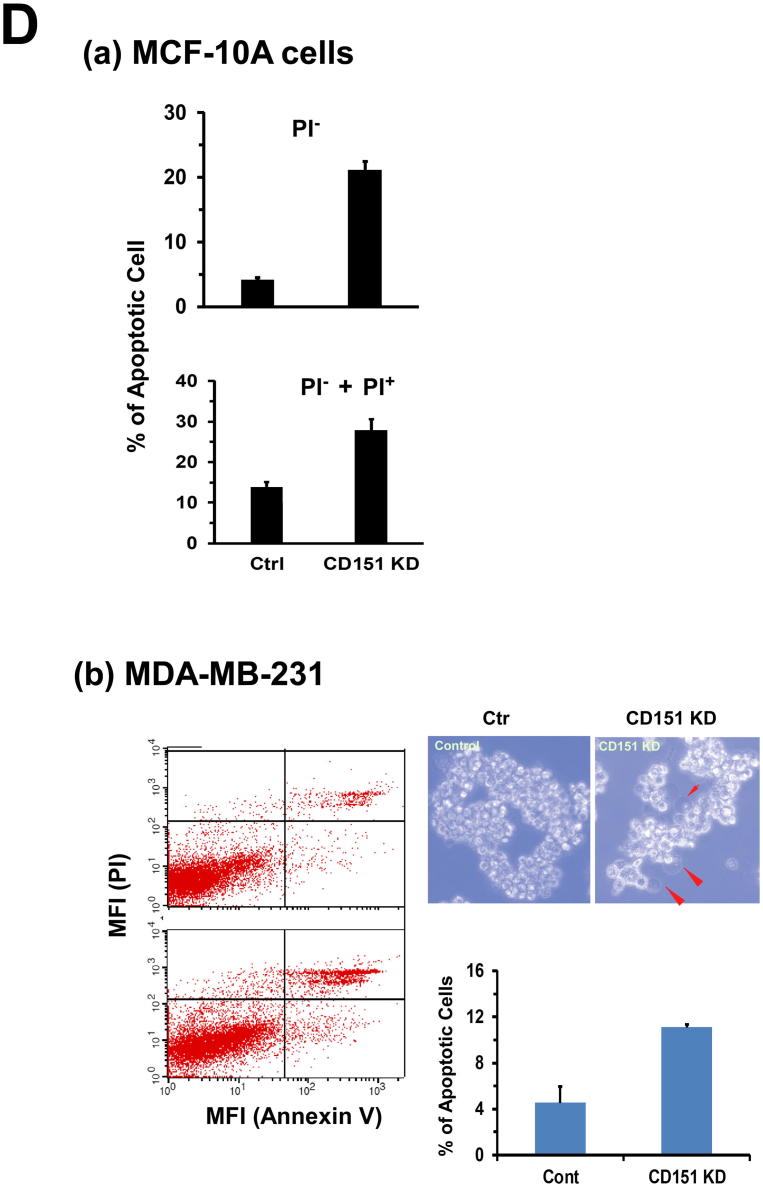
Fig. 6.
A link between CD151 and the tumor-initiating capability of breast cancer cells. A H&E staining of mammary tumor tissues. Scale bar, 100 μm. B Images of primary cell culture of mammary tumors from the MMTV-Wnt1 mice. The fresh tumor tissues were surgically removed, digested overnight in collagenase, filtered with 40 µm strainer, followed by additional 3 days of culture prior to the imaging. C Images of tumorspheres formed by MCF-10A cells. MCF-10A cells were infected with control (a) and CD151-specific shRNA-expressing (b) lentiviral vector to express CD15 shRNA (KD). The Cd151 KD cells were further infected with retroviral-based CD151 wildtype (RX) and an integrin binding-defective mutant (EC2). Scale bar: 50 μm. D Effect of CD151 knockdown (KD) on cell survival. Cells with or without CD151knckdown were analyzed for difference in apoptotic cell death by flow cytometry-based analysis of cell staining of APC-conjugated Annexin V and PI. on: (a) MCF-10 cells were cultured for 24 hrs prior to the analysis. (b) MDA-MB-231 cells were kept under ultra-low adhesion for 24hrs, and imaged or analyzed on flow cytometry for apoptosis. Images of typical apoptotic cells, arrow-pointed. Values: mean ± SEM (n = 3). *: p < 0.05.