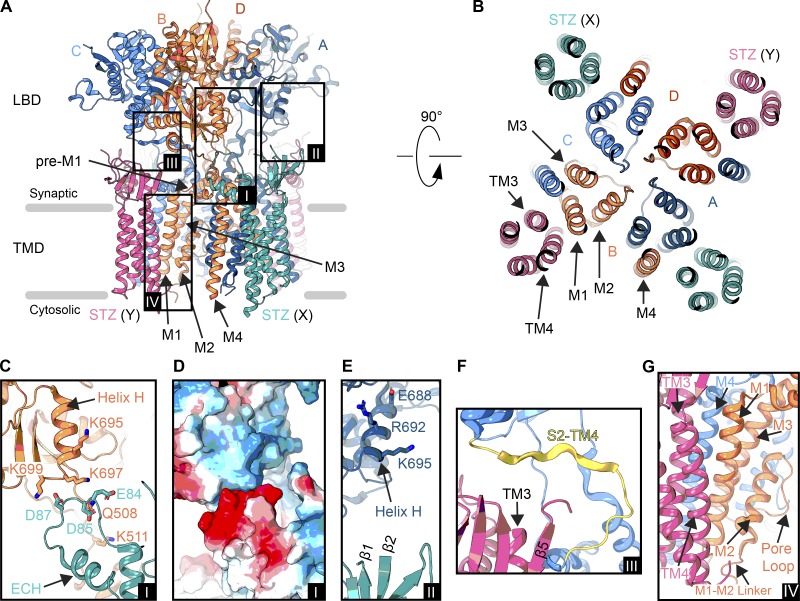
Figure 6.
Interfaces in an AMPAR–STZ complex. (A) Structure of an AMPAR (GluA2 homotetramer) bound to four STZ molecules in ribbon representation viewed parallel to the membrane (PDB accession no. 5WEO). The ATD has been excluded. Each GluA2 subunit is colored individually (A, dark blue; B, coral; C, light blue; D, dark orange), and STZ subunits are colored teal (X site) or pink (Y site). Boxed are regions illustrated in C–G. (B) Extracellular view on the TMD from right above the Q/R site. Membrane segments of one AMPAR subunit (B subunit M1-M4) and one STZ subunit (Y site, TM1-4) are labeled. (C) Interface between the LBD of the B subunit from the AMPAR and the β4-TM2 loop preceding the ECH of a X-site STZ molecule (A, inset I). (D) Electrostatic surface for the region shown in C, blue being positively charged, red negatively charged, and white neutral (A, inset I). (E) Potential interaction between an X-site TARP β1-β2 loop and A subunit LBD helix H (A, inset II). (F) Interface between a Y-site TARP TM3-β5 loop and S2-TM4 linker in the C subunit (A, inset III). (G) AMPAR–TARP interface in the TMD (A, inset IV).