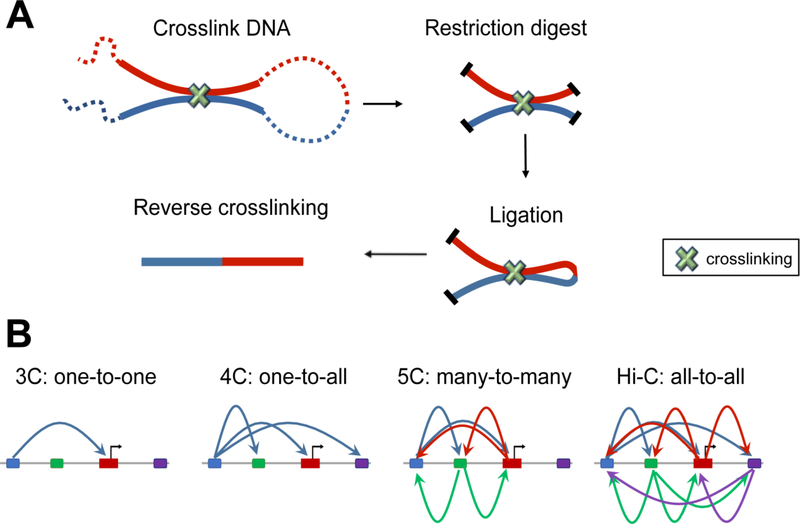
Figure 1. Chromosome conformation capture based techniques.
(A) In Chromosome conformation capture (3C), three dimentional proximal DNA fragments are crosslinked and digested while in the nucleus. Open ends of DNA fragments are then repaired and chimeric fragments are ligated, which allows the detection of linearly-distant genomic segments that reside in spatial proximity. (B) The 3C-based techniques have evolved to focus on interactions between a single pair of genomic loci (3C), between one locus and all other genomic loci (4C), between all restriction fragments within a given region (5C), or between all possible pairs of fragments across the genome (Hi-C).