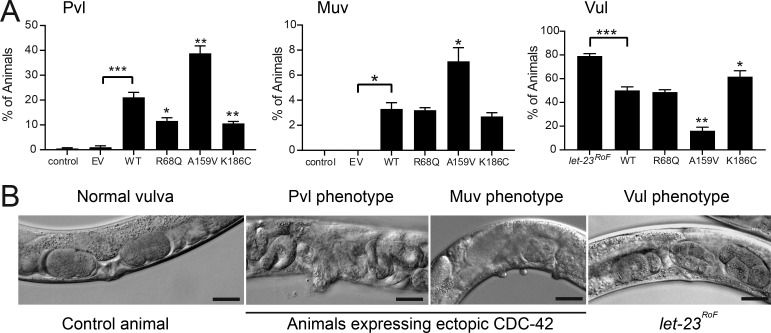
Figure 6.
p.R186C affects C. elegans vulval development. (A) Hypomorphic effect of the mutation on pathways controlling C. elegans vulval development. Compared with WT CDC-42, the K186C mutant induces a less penetrant Pvl phenotype and less efficiently rescues the Vul phenotype of animals carrying a hypomorphic let-23/EGFR allele, indicating a hypomorphic behavior on multiple signaling pathways. The R68Q and A159V mutants, representative of group I (substitutions characterized by impaired binding to regulators and effectors) and group II (gain-of-function changes) mutations, respectively, are shown for comparison. Error bars indicate SEM of three independent experiments. Asterisks specify significant differences between animals expressing WT CDC-42 and those expressing the empty vector (EV) or the let-23(sy1) allele (*, P < 0.05; ***, P < 1.2e-6; two-tailed Fisher’s exact test), and between animals expressing WT and mutant CDC-42 (*, P < 0.05 [Muv] or P < 0.005 [Pvl and Vul]; **, P < 0.00002 [Pvl] or P < 3.2e-6 [Vul]). Number of animals are reported in Table S4. (B) Representative images of C. elegans phenotypes. Scale bars, 20 µm.