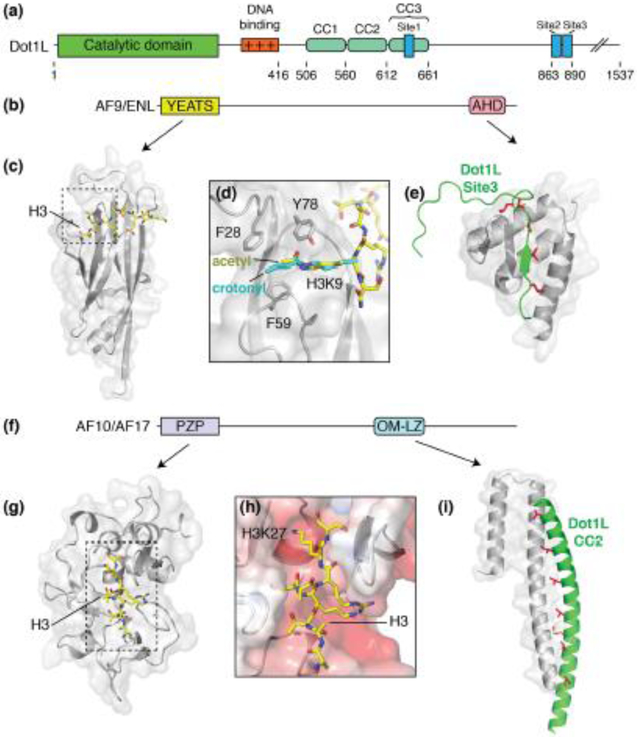
Figure 2. Dot1L partner proteins.
(a) Domain architecture schematic of Dot1L. (b) Domain architecture schematic for Dot1L partners, AF9 and ENL. (c) Structure of the AF9 YEATS domain (PDB: 4TMP, gray) bound to acetylated H3K9 (yellow sticks). (d) Close up view of the acetylated H3K9 binding site. Crotonylated H3K9 (PDB: 6MIM) is shown in cyan. (e) Structure of the AF9 AHD (PDB: 2MV7, gray) domain bound to Dot1L site3 (green). Buried hydrophobic residues are colored red and shown as sticks. (f) Generalized domain architecture schematic for AF10 and AF17. (g) Structure of the AF10 PZP domain (PDB: 5DAH, gray) bound to an unmodified H3 peptide (yellow sticks). (h) Close up view of the AF10 PZP H3 binding groove. The surface of AF10 is colored according to electrostatic potential. (i) Structure of the AF10 OM-LZ motif (PDB: 6CKO, gray) bound to the CC2 of Dot1L (green). Buried hydrophobic residues are colored red and shown as sticks.