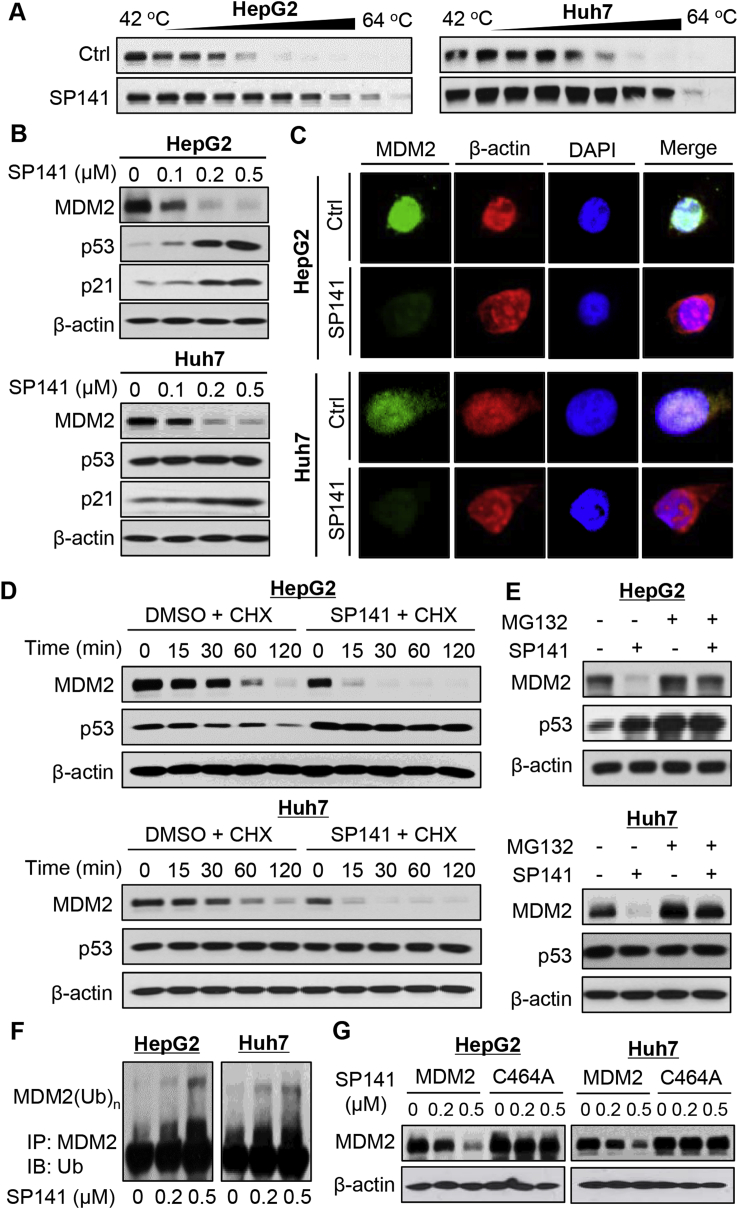
Figure 2.
SP141 induces MDM2 degradation in human HCC cells. (A) HepG2 and Huh7 cells were exposed to 1 μM of SP141 for 2 h, followed by cellular thermal shift assays. (B) HCC cells were exposed to various concentrations of SP141 for 24 h. The protein expression levels of MDM2, p53, and p21 were determined. (C) The HepG2 and Huh7 cells were exposed to vehicle or SP141 (0.5 μM) for 24 h, followed by immunofluorescence detection of MDM2. (D) The cells were treated with or without SP141 for 24 h, followed by exposure to a protein synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide (CHX, 15 μg/mL). The protein levels of MDM2 and p53 were detected at the indicated times after exposure to CHX. (E) The HepG2 and Huh7 cells were treated with or without SP141 (0.5 μM) for 24 h. They were then exposed to MG-132 (25 μM), a proteasome inhibitor, for an additional 6 h. The protein levels of MDM2 and p53 were detected by Western blotting. (F) The cells were co-transfected with MDM2 and ubiquitin plasmids, followed by treatment with SP141 (0, 0.2 and 0.5 μM) for 24 h. Then the cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-MDM2 antibody. The ubiquitinated MDM2 was detected using an anti-ubiquitin antibody. (G) The cells were transfected with a wild-type MDM2 plasmid or a mutant MDM2 plasmid (C464A) without E3 ligase activity, followed by exposure to SP141 (0, 0.2 and 0.5 μM) for 24 h. The MDM2 protein levels were detected. All assays were performed in triplicate and repeated three times.