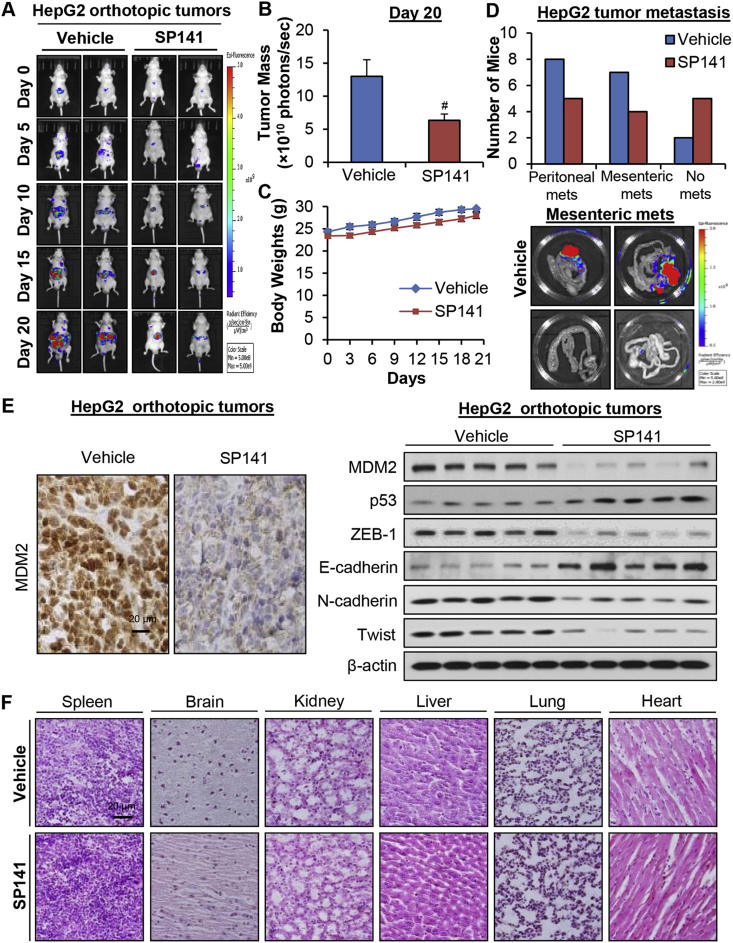
Figure 5.
SP141 suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in an orthotopic model of HCC. HepG2-GFP cells were implanted orthotopically into the left liver lobe of nude mice. Nude mice bearing HepG2-GFP orthotopic tumors were administered SP141 by i.p. injection at a dose of 40 mg/kg/d, 5 d/wk for 20 days. (A) Tumor size was monitored once every 5 days by fluorescence imaging via an IVIS in vivo imaging system. (B) On Day 20, the average tumor mass (determined by the detected photons/sec) of the SP141-treated mice was compared with that of the control mice. (C) The mice were monitored for changes in body weight as a surrogate marker for toxicity. (D) At the termination of the experiments, the numbers of mice with metastasis to the peritoneum and mesentery were counted. Representative images showing mesenteric metastasis are presented. (E) The tumors were excised and analyzed for the expression of proteins of interest by immunohistochemistry (scale bar, 20 μm) and Western blotting assays (each lane represents a different tumor sample). (F) Representative H&E-stained tissue and organ samples are presented (scale bar, 20 μm). (*P < 0.05 and #P < 0.01).