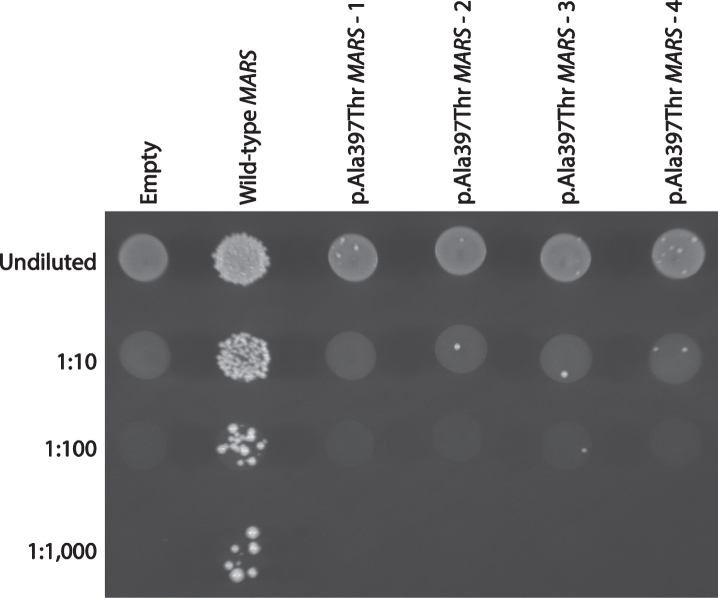
Fig.2.
The p.Ala397Thr MARS allele displays a loss-of-function effect in yeast complementation studies. Yeast lacking endogenous Mes1 (the yeast ortholog of MARS) were transformed with vectors containing wild-type or p.Ala397Thr MARS, or a vector with no MARS insert (‘Empty’). Four independent p.Ala397Thr MARS expression constructs were transformed, grown in selective media, and plated undiluted or diluted (1 : 10, 1 : 100, or 1 : 1,000) on media containing 5-FOA. This system allows for assessment of the ability of experimental alleles to support yeast cell growth in vivo (in the absence of the yeast MARS ortholog, Mes1). The haploid yeast strain deleted for the endogenous Mes1 locus was transformed with a pRS315 experimental vector containing the LEU2 gene and either: (1) no MARS insert (‘Empty’); (2) wild-type MARS; or (3) p.Ala397Thr MARS. Wild-type MARS supported robust cellular growth, while the vector with no MARS insert did not. These data indicate that the experimental vector harbors a functional wild-type copy of MARS and that Mes1 is an essential gene, respectively. In contrast, p.Ala397Thr MARS supported very little yeast cell growth, consistent with this being a loss-of-function allele.