Fig. 3.
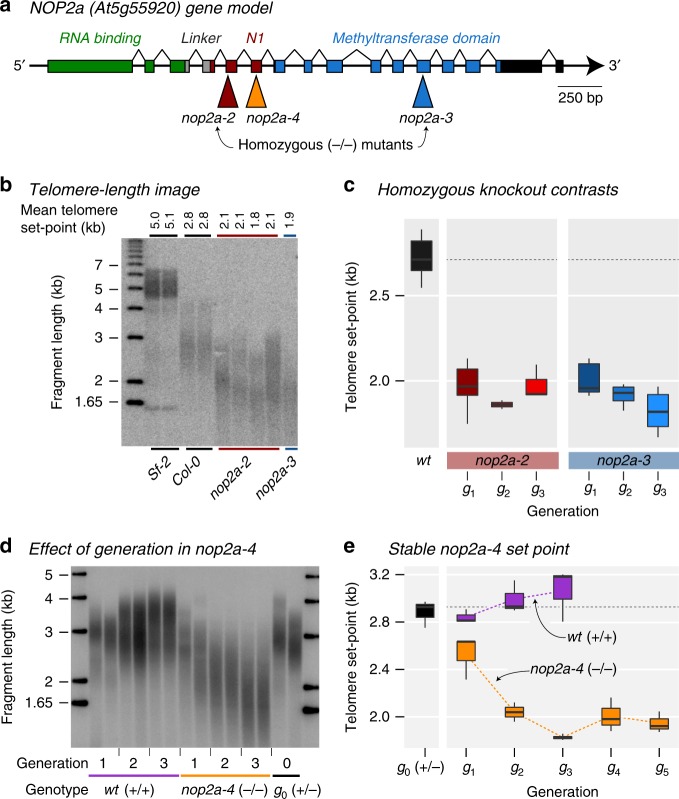
Inactivation of AtNOP2A gene leads to the establishment of a new shorter telomere length set point. a Representation of the Arabidopsis NOP2A/OLI2 gene model. Colored boxes represent exons; black lines, introns; and black boxes, untranslated regions. Positions of T-DNA insertion sites and the corresponding mutant line numbers are indicated. Predicted S-adenosyl-l-methionine-dependent methyltransferase functional domains are indicated on top. b A representative TRF southern blot for Sf-2 and Col-0 wild types and two NOP2A/OLI2 homozygous T-DNA mutant lines (nop2a-2 and nop2a-3) is shown, where mean telomere length (mean TRF) for each individual analyzed plant is indicated at the top. Molecular weight DNA markers (in kb) are shown on the left. c The distributions of telomere length in ≥3 biological replicates of the Col-0 wild type and the two homozygous mutants are shown in boxplots (midline = median, box = interquartile range (IQR), whiskers = 1.5*IQR). Across generations, T-DNA mutants show shorter telomere length set point than the corresponding wild type Col-0 genotype. d An example of a TRF southern blot for telomere length analysis of several consecutive generations of homozygous nop2a-4−/− mutants. Seeds of a single self-pollinated heterozygous nop2a-4+/− plant were grown to identify wild type, heterozygous and homozygous G1 progeny, which were then used to generate corresponding G2 and G3 mutant generations by single seed descent. e, T-DNA mutants with the null nop2a-4 allele displayed significantly shorter telomeres after only a single generation of self-pollination, but established a new stable set point by the third generation of mutants.