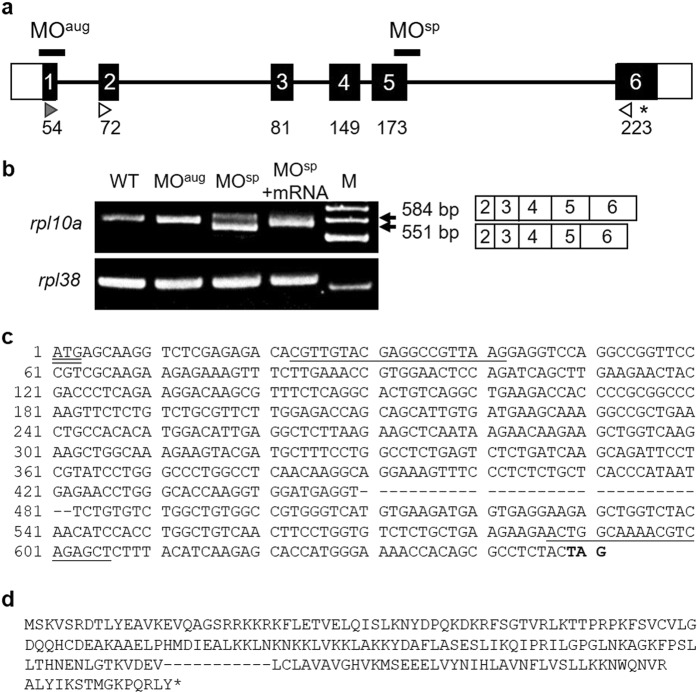
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of the zebrafish rpl10a gene structure. White boxes represent the untranslated regions, while the translated region is shown with black boxes. The start codon (gray arrowhead) and stop codon (asterisk) positions are presented. The white arrowheads are marked at the position of the MOsp detection primer, and the arrowheads indicate the direction of PCR polymerization. The positions of the designed MOaug and MOsp are indicated. (b) RT-PCR analysis of rpl10a in MO-injected (MOaug, MOsp), rescued (MOsp + mRNA) and wild-type embryos; rpl38 was amplified as a control. M was shown as a 100 bp ladder. A smaller PCR product (551 bp) was observed from MOsp-injected embryos because 33 bp of exon 5 was skipped; the wild-type product was 584 bp (primers were designed to obtain products smaller than the full-length gene). (c) The nucleotide sequences of rpl10a cDNA are presented. The hyphens displayed 33 bps of exon 5 that were deleted after MOsp injection. The underline shows the position of primer sequences. The start codon and stop codon appeared in double underline and bold text, respectively. (d) The amino acids were predicted using the translation tool from www. ExPASy.com. The 11 amino acids were predicted to be removed after deletion. Hyphens showed deleted amino acids, and the stop codon is shown in an asterisk.