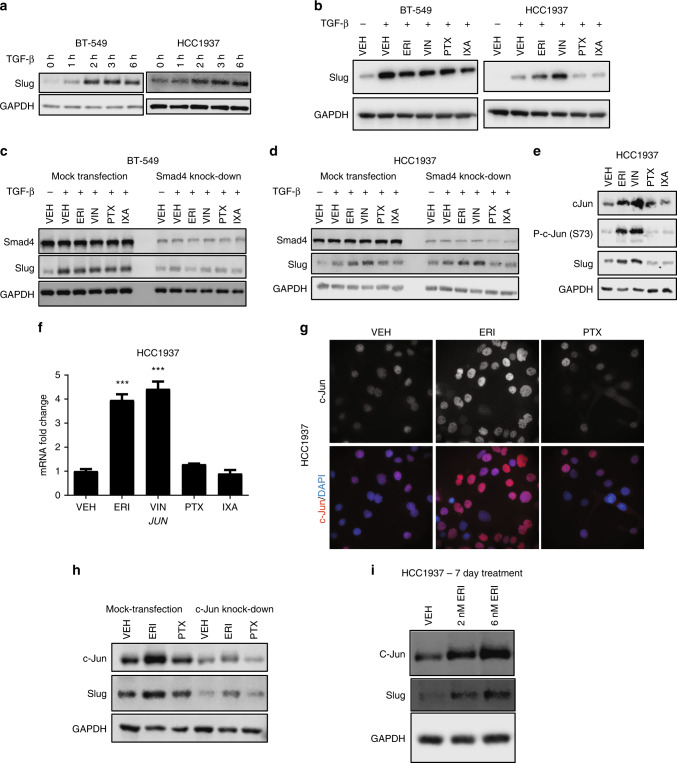
Fig. 4.
Microtubule targeting agents differentially impact Slug expression in breast cancer cell lines. a Western blot analysis of Slug from BT-549 and HCC1937 cells that were serum-starved for 18 h, and then stimulated with TGF-β for the indicated times. b Western blot analysis of Slug and GAPDH from whole-cell lysates from BT-549 and HCC1937 cells that were serum-starved for 18 h, pre-treated with microtubule targeting agents for 2 h followed by a 3 h stimulation with TGF-β. c, d Smad4 was transiently knocked-down by siRNA in BT-549 and HCC1937 cells. Cells were then serum-starved for 18 h, pre-treated with microtubule targeting agents for 2 h, then stimulated with TGF-β for 3 h. Cell lysates were subject to immunoblotting for Smad4, Slug, and GAPDH. e Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates from HCC1937 cells that were serum-starved for 18 h and treated with microtubule targeting agents for 5 h. Immunoblots were probed for total and phosphorylated forms of c-Jun, Slug, and GAPDH. f mRNA analysis of JUN transcript in HCC1937 cells that were serum-starved for 18 h and then treated with microtubule targeting agents for 4 h (N = 2). Data are reported as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance compared to vehicle controls was determined using a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test (***p < 0.001). g HCC1937 cells were serum-starved for 18 h and then treated with microtubule targeting agents for 5 h. Immunofluorescence images of c-Jun and DAPI are shown. h c-Jun was transiently knocked-down in HCC1937 cells by siRNA. Cells were serum-starved for 18 h and then treated with microtubule targeting agents for 5 h. Cell lysates were subject to immunoblotting for c-Jun, Slug, and GAPDH. i Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates from HCC1937 cells treated with vehicle or eribulin for 7 days. Immunoblots were probed for Slug, c-Jun, and GAPDH