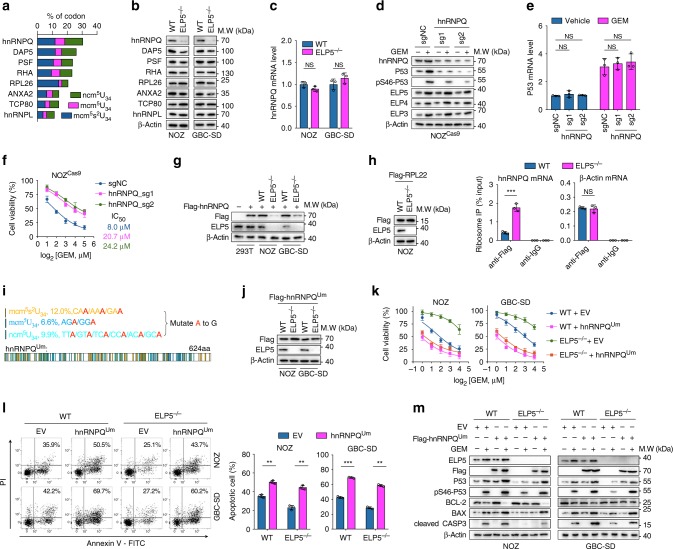
Fig. 6.
ELP5 mediates wobble U34 tRNA modification-dependent translation of hnRNPQ. a The content of U34 cognate codons of the hnRNPQ ORF was the most enriched in P53 ITAFs. ITAF, IRES trans-acting factor. b, c ELP5 depletion downregulated the expression level of hnRNPQ protein (b), but not mRNA (c). d, e The hnRNPQ knockout significantly reduced P53 protein expression and activation under GEM treatment (d), but no effects were observed in the expression of Elongator subunits (d) and P53 mRNA (e). f The hnRNPQ knockout exhibited GEM resistance in NOZCas9 cells. g Exogenous hnRNPQ with a WT ORF sequence was poorly expressed in ELP5-depleted cells. h WT and ELP5-depleted NOZ cells stably expressed Flag-RPL22 (left panel) to perform ribosome immunoprecipitation followed by RT-qPCR, and the results showed ribosome accumulation in hnRNPQ mRNAs in ELP5−/− cells, but not in control mRNAs (β-Actin) (right panel). i Schematic drawing of the wobble U34 cognate codon mutation (Um) in the hnRNPQ ORF sequence (hnRNPQUm). j Flag-hnRNPQUm was expressed normally in both WT and ELP5−/− cells. k, l Successfully overexpressed hnRNPQUm could promote or rescue GEM sensitivity (k) and GEM-induced apoptosis (l) in WT and ELP5−/− cells, respectively. m Overexpression of hnRNPQUm promoted P53 accumulation and activation in ELP5-depleted GBC cells. Data represent the mean ± S.D., n = 3 independent experiments in c, e, f, h, k, l, error bars represent S.D. Unpaired Student’s t tests were used in c, e, h, l (NS, non-significant, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001).