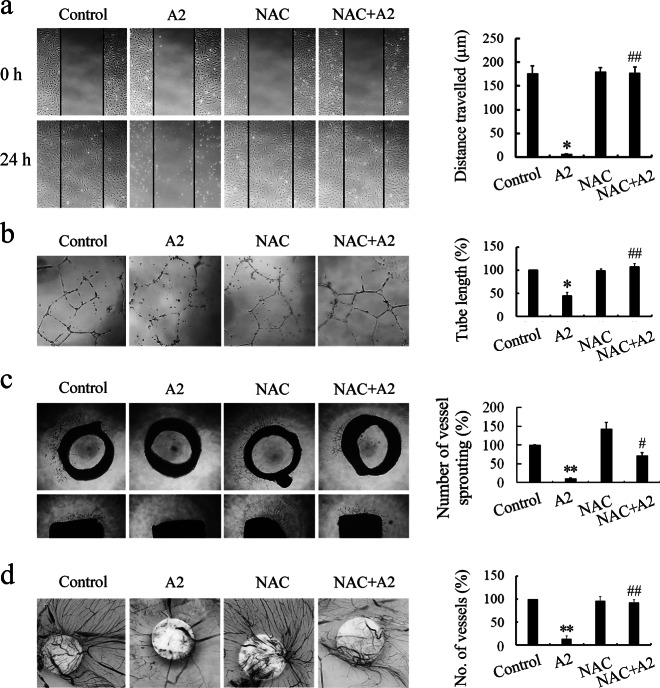
Fig. 8.
Scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) reverses the antiangiogenic effects of curcumin analog A2 in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo. a Wound healing assay was used to assess the migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or curcumin analog A2 (20 μM) in the presence or absence of NAC (10 mM). These photos were taken under a phase-contrast microscope ( × 40). Top photos were taken immediately after scraping. Bottom photos were taken at 24 h after scraping. Histogram shows the cell migration distance data. (n = 3; *P < 0.05 vs. Control; ##P < 0.01 vs. A2). b HUVECs were plated on Matrigel, then the cells were treated with DMSO or curcumin analog A2 (20 μM) in the presence or absence of NAC (10 mM) for 24 h. These photos were taken at 24 h after treatment under a phase-contrast microscope ( × 40). Histogram shows the relative total length of tubes. (n = 3; *P < 0.05 vs. Control; ##P < 0.01 vs. A2). c Rat aortic rings were incubated with DMSO or curcumin analog A2 (20 μM) in the presence or absence of NAC (10 mM). These photos were taken at day 7 after treatment under a phase-contrast microscope ( × 40). Top photos show the aortic rings placed horizontally in Matrigel. Bottom photos show the aortic rings placed vertically in Matrigel. Histogram shows the relative total number of vessels sprouting. (n = 3; **P < 0.01 vs. Control; #P < 0.05 vs. A2). d New blood vessels formation was detected using chicken CAM assay. Sterilized filter paper disks saturated with DMSO or curcumin analog A2 (20 μM) in the presence or absence of NAC (10 mM) were placed on the CAMs. After incubation for 2 days, the CAMs were removed for further analysis. These photos were taken using a Canon EOS 550D Digital SLR camera. Histogram shows the relative number of new blood vessels on the filter paper disks. (n = 3; **P < 0.01 vs. Control; ##P < 0.01 vs. A2)