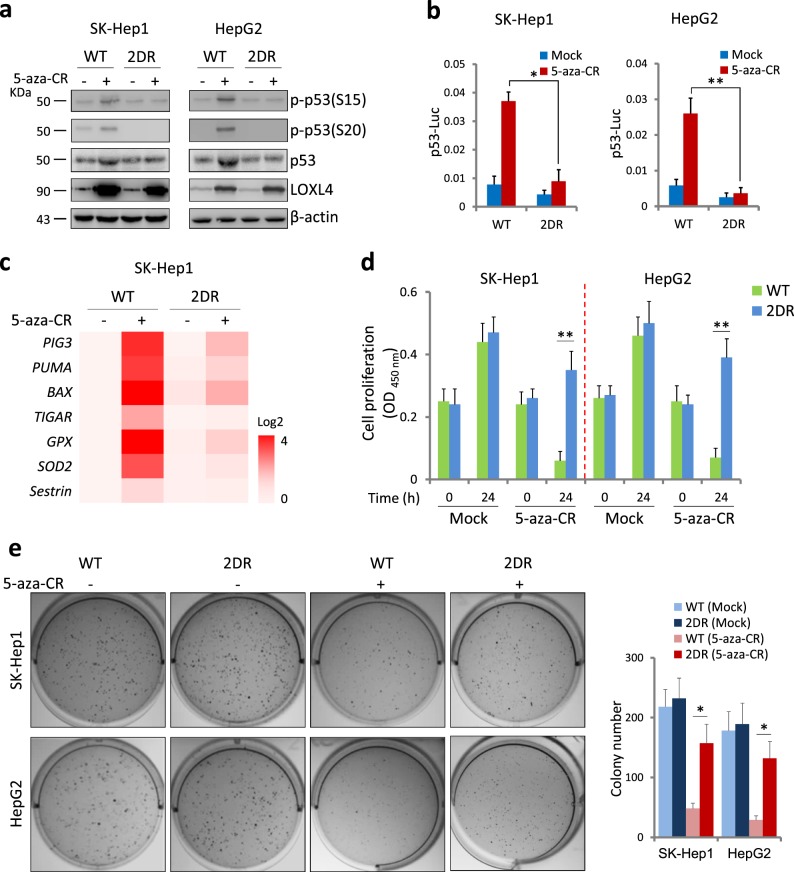
Fig. 5.
LOXL4 is required for p53 activation, which depends on LOXL4-p53 interaction. a Western blotting analysis of cells with wild-type or 2DR (D677/679R) mutated LOXL4 in response to 5-aza-CR (5 μM) treatment for 24 h. The strategies for creating D677/679R (2DR) mutant LOXL4 in SK-Hep1 and HepG2 cells using CRISPR/Cas9 are described in Fig. S7. The indicated antibodies were used to examine LOXL4 protein levels and p53 activation. Experiments were independently performed three times. b 2DR mutation abolished p53 activation in response to 5-aza-CR (5 μM) treatment for 24 h. The cell lines used to measure p53-luciferase reporter activity are originated from Fig. 5a. Data were from three independent experiments performed in triplicate; error bars represent SEM. c Gene expression induced by 5-aza-CR (5 μM) treatment for 16 h. Several downstream p53 target genes were detected via quantitative real time PCR. Experiments were independently performed three times. d Cell proliferation of SK-Hep1 and HepG2 cells with or without 5-aza-CR (5 μM) treatment. A CCK-8 assay was used to measure cell proliferation. Data were from three independent experiments performed in triplicate; error bars represent SEM. e Colony formation of SK-Hep1 and HepG2 cells with or without 5-aza-CR (2 μM) treatment for two weeks. The total number of colonies in a six-well plate was calculated using ImageJ software (version 1.8.0). Data were from three independent experiments performed in triplicate; error bars represent SEM