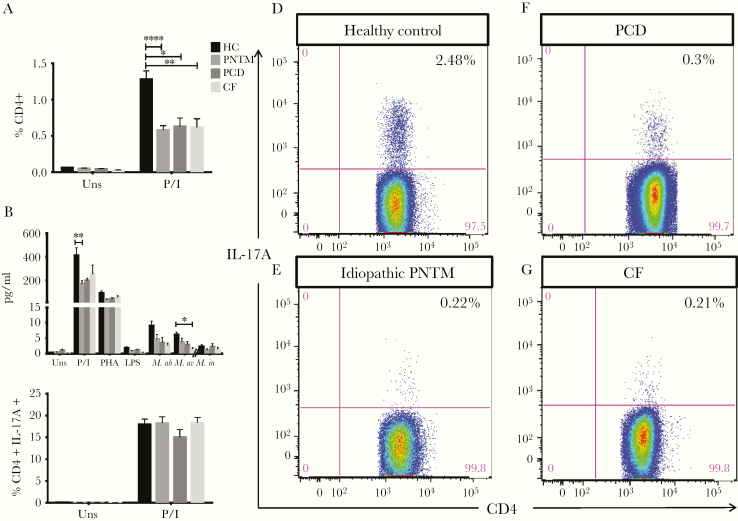
Fig 2.
Th17 responses were decreased in patients with PNTM disease. The percentages of IL-17A-expressing CD4+ cells were significantly lower in patients with idiopathic PNTM disease, PCD, and CF compared with healthy controls in response to PMA + ionomycin stimulation (A). Supernatant IL-17A level also was significantly reduced in idiopathic PNTM patients in response to PMA + ionomycin stimulation, and in CF patients in response to M. avium stimulation as compared with healthy controls (B). The frequencies of IFN-γ-expressing CD4+ IL-17A+ cells were comparable among the groups (C). Representative plots show expression of IL-17A in CD4+ T cells in a healthy volunteer (D), an idiopathic PNTM patient (E), a PCD patient (F) and a CF patient (G). Both (D) and (E) were performed in the same experiment, while (F) and (G) were performed simultaneously in another experiment. HC indicates healthy controls; uns, unstimulated; PHA, phytohemagglutinin + IL-12; P/I, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate + ionomycin; M.ab, Mycobacterium abscessus (MOI: 10); M.av, Mycobacterium avium (MOI: 10); M.in; Mycobacterium intracellulare (MOI: 0.2). Data are presented as means; error bars show standard error. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.