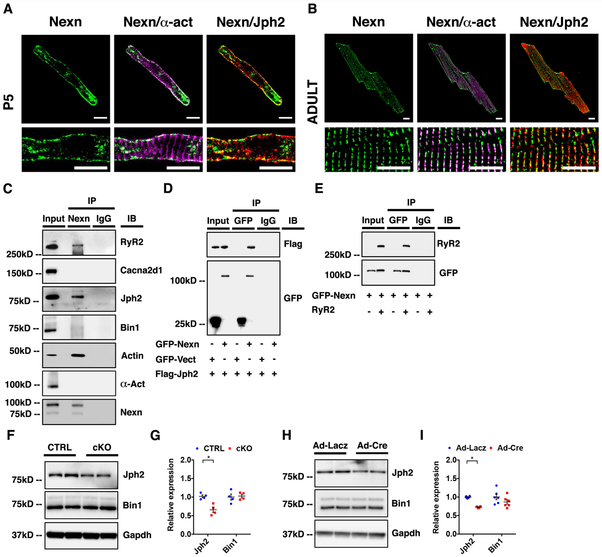
Figure 5. NEXN localizes to the JMC and interacts with junctional SR proteins.
(A) Representative confocal images of a P5 CTRL cardiomyocyte showing how NEXN in green do not co-localize with α-actinin (α-act) in magenta, while co-localizing with Jph2 in red; scale bars 10μm. (B) Representative confocal images of an adult CTRL cardiomyocyte in the lower panels showing dyadic localization of NEXN; scale bars 10μm.Fig (C) Co-immunoprecipitation of NEXN with putative binding partners using heart tissue lysates. (D) Immunoprecipitation of GFP-tagged NEXN and Flag-tagged Jph2 co-expressed in HEK293 cells. (E) Immunoprecipitation of GFP-tagged NEXN and tetracycline (10 ug/ml, 24 hours) induced RyR2 co-expressed in a stable tetracycline inducible HEK293 cell line expressing RyR2. (F-H) Western blot representative images and (G-I) quantification graphs of Ca2+-handling proteins from (F-G) E18.5 mouse ventricles (n = 4) and from (H-I) isolated neonatal NEXNf/f cardiomyocytes treated with Ad-Lacz or Ad-cre virus (n=6). (*) Statistically significant differences with P value < 0.05.