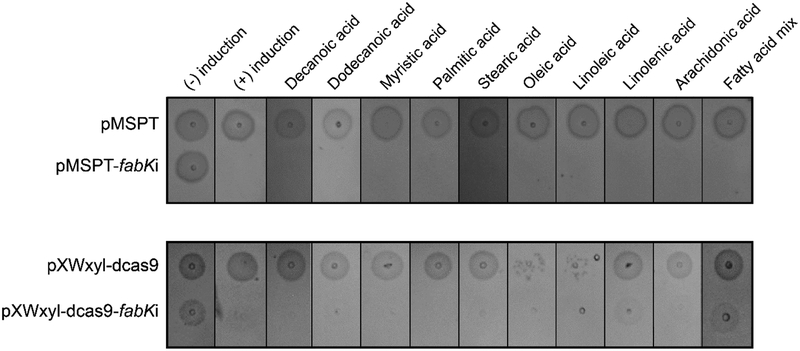
Figure-2: Effect on cell growth in presence of antisense fabK RNA and exogenous fatty acids.
Overnight cultures of C. difficile CD630 harbouring respective plasmids were analyzed on BHI agar plates with respective concentrations of fatty acids. Antisense RNA expression was induced by 0.256 μg/mL ATc (top panel) or 1% (w/v) xylose (bottom panel). Cell viability was tested in presence of individual fatty acids i.e. decanoic acid (256 μM), dodecanoic acid (8 μM), myristic acid (16 μM), palmitic acid (256 μM), stearic acid (256 μM), oleic acid (32 μM), linoleic acid (16 μM), linolenic acid (8 μM) and arachidonic acid (8 μM). The fatty acid mixture was used at sub-inhibitory concentrations of individual fatty acids; in some cases partial growth recovery was observed with the xylose inducible Crispr-interference; with addition of 1% (w/v) xylose, cells were more sensitive to oleic acid and linoleic acid.