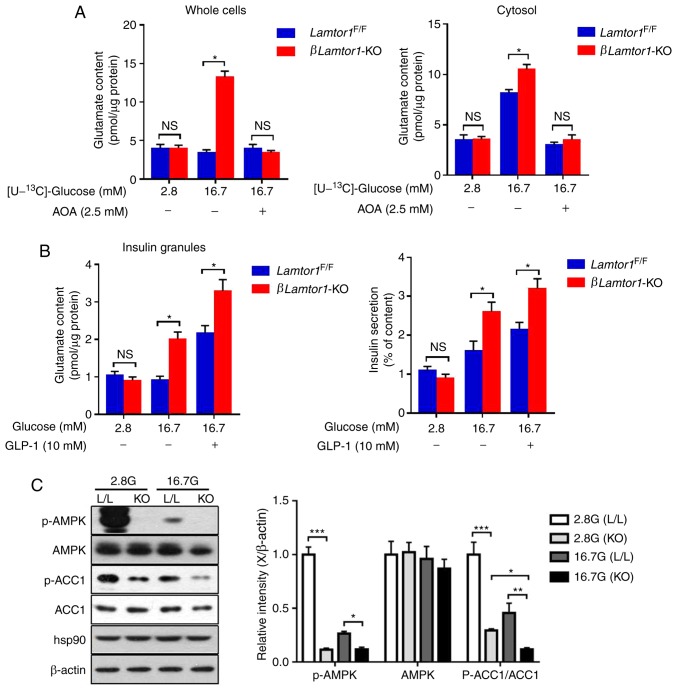
Figure 5.
Lamtor1 deficiency in pancreatic β-cells amplifies insulin secretion by increasing glutamate production and ACC1 activity. (A) Effects of amino-oxyacetate (2.5 mM) on the content of glutamate isotopomers in whole cells and the cytosol in isolated Lamtor1-deficient and control pancreatic β-cells. n=6. (B) Changes in glutamate content in the insulin granules and insulin secretion under glucose stimulation in the absence or presence of glucagon-like peptide 1 (10 nM). (C) Western blots showing phosphorylated adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase, total adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase, phosphorylated ACC1, total ACC1, heat-shock protein 90 and β-actin protein levels in Lamtor1F/F and βLamtor11-KO mouse islets under low- and high-glucose stimulation. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, n=6. ACC1, acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1; p-ACC1, phosphorylated ACC1; AOA, aminooxyac-etate; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; AMPK, adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase; p-AMPK, phosphorylated AMPK; hsp90, heat-shock protein 90; NS, no significance.