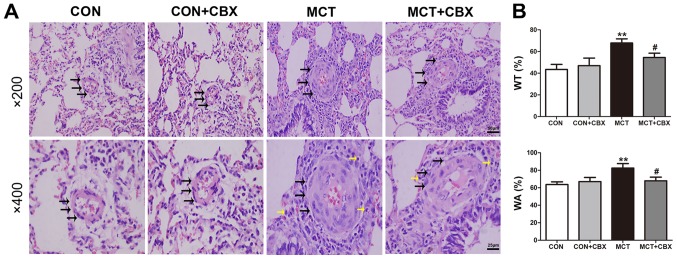
Figure 3.
Administration of CBX prevents MCT-induced remodeling of medium-sized pulmonary arterioles. (A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining indicating the histopathological changes in medium-sized pulmonary arterioles at magnification, ×200 (scale bar=50 µm; upper panel) and magnification, ×400 (scale bar=25 µm; lower panel). MCT-treated animals had obliterated vessels (black arrows). No obliteration was observed in the control rats or rats treated with a single intraperitoneal injection of CBX. CBX administration did not decrease lumen obliteration of medium-sized pulmonary arterioles. Black and yellow arrows indicate pulmonary arterial obliteration and perivascular infiltration of inflammatory cells in medium-sized pulmonary arterioles, respectively. (B) WT% and WA% were significantly increased in MCT-treated rats, and CBX treatment of the MCT rats significantly decreased WT% and WA% in the medium-sized pulmonary arteries compared with those in MCT-treated animals. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean of 6 rats/group. **P<0.01 vs. control. #P<0.05 vs. MCT group. CBX, carbenoxolone; MCT, monocrotaline; CON, control; WT%, percentage of vascular wall thickness; WA%, percentage of the vascular wall area.