Figure 2.
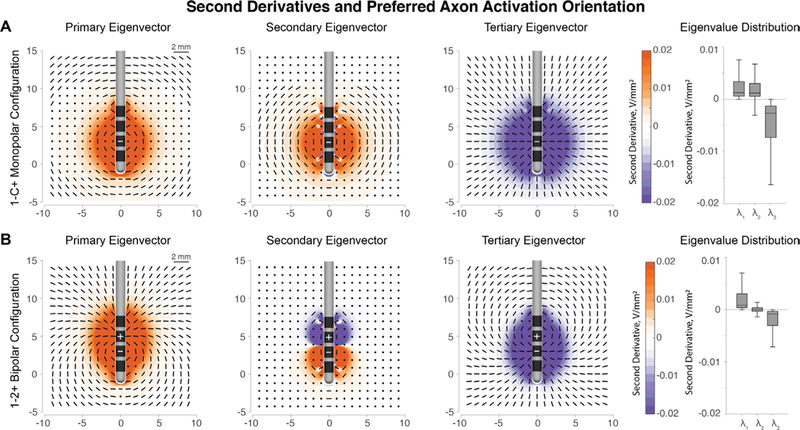
(A) Primary, secondary, and tertiary eigenvector orientations for cathodic stimulation at contact 1 of the Medtronic 3389 lead. Longitudinal and latitudinal fibers (passing fibers) have positive second derivatives, which correspond to an increased likelihood of firing. The orthogonal direction defined by the tertiary eigenvector has negative second derivatives. The median amplitude of the tertiary eigenvalues is twice that of the primary and secondary eigenvalues, implying large inhibition of orthogonal fibers. (B) Eigenvector directions remain the same around the cathode, but the activation patterns are reversed around the anode. Note: box-whisker plots are plotted without outliers for clarity.
