Figure 5.
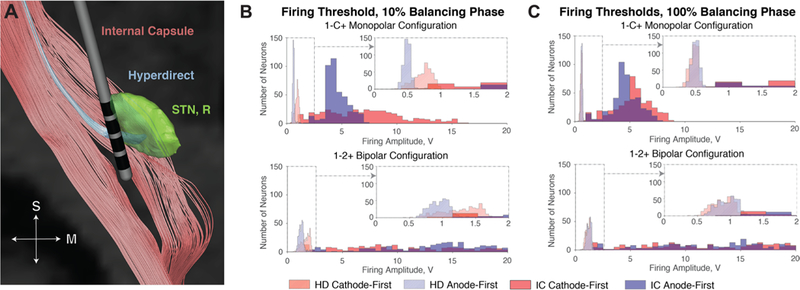
(A) Visualization of HD and IC tracts with respect to the STN (right) and lead. (B) Firing threshold histograms for HD and IC tracts given cathodic and anodic stimulation for 10% balancing. Anodic stimulation reduces threshold voltage of orthogonally oriented fibers. As a result, the HD is activated by a smaller voltage with anodic stimulation rather than cathodic stimulation. The orthogonal components of the IC are activated at lower thresholds as well, but bipolar stimulation reduces the spread of activation in the IC. (C) Firing histograms using symmetrically balanced pulses exhibit lower firing thresholds for both the HD and IC, but bipolar stimulation avoids the IC.
