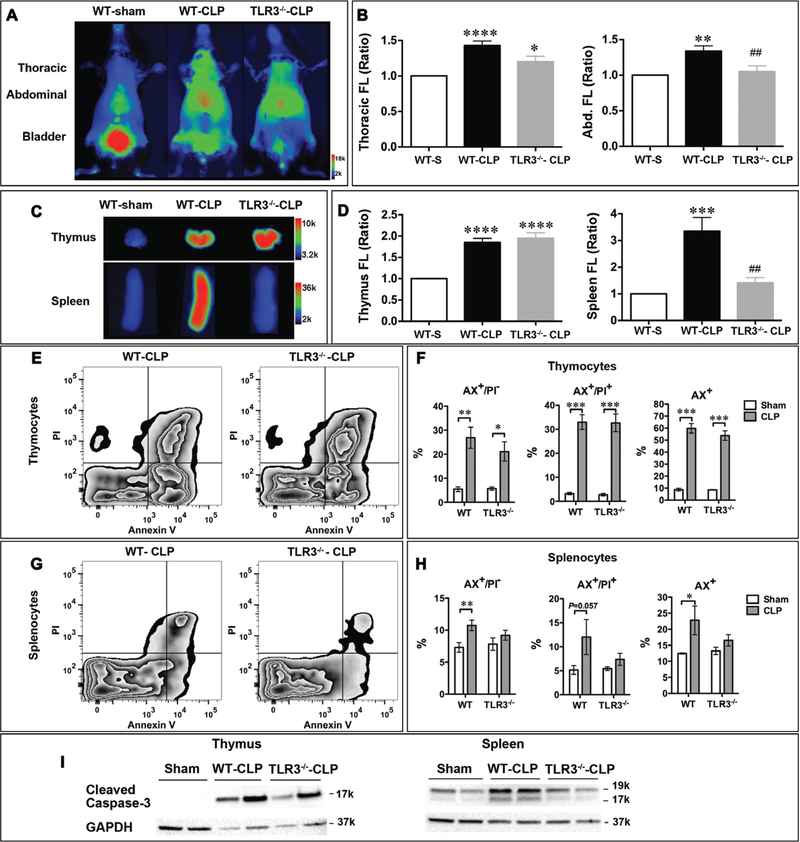
Figure 5.
Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) deficiency reduced cell death in the spleen. Wild-type (WT) and TLR3−/− mice were subjected to sham or cecum ligation and puncture (CLP) surgery (severe model). AV-750 imaging in vivo, organs ex vivo, and flow cytometry were applied to detect cell death at 24 hr. A, Representative pictures of in vivo AV-750 imaging. B, AV-750 fluorescence signal in vivo was quantified as ratio over sham. AV-750 uptake was significantly increased in sepsis in both the thorax and the abdominal regions. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001 versus sham (WT-S). ##p < 0.01 versus WT-CLP. n = 3 in the sham group, n = 9 in the WT-CLP group, and n = 7 in the TLR3−/−-CLP group. C, Representative ex vivo AV-750 imaging. Right after in vivo imaging, thymus and spleen were harvested and exposed in an IVIS imaging system. D, Ex vivo AV-750 fluorescence signal is quantified as ratio over sham. ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001 versus sham (WT-S). n = 3 in the sham group, n = 9 in the WT-CLP group, and n = 7 in the TLR3−/−-CLP group. ##p < 0.01 versus WT-CLP. E, Representative pictures of flow cytometry data in thymocytes. F, WT and TLR3−/− septic mice showed the same level of cell death in thymocytes. n = 3 in the sham group, n = 9 in the WT-CLP group, and n = 7 in the TLR3−/−-CLP group group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001. G, Representative pictures of flow cytometry data in splenocytes. H, Sepsis led to cell death in WT splenocytes. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01. TLR3 deficiency prevented the development of splenocyte cell death induced by sepsis. n = 3 in the sham group, n = 9 in the WT-CLP group, and n = 7 in the TLR3−/−-CLP group. I, Apoptosis was reduced in TLR3−/− septic spleen as evidenced by attenuated caspase-3 cleavage, but not in septic thymus. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) served as protein loading control. Abd. = abdominal, AX= fluorescein-labeled annexin V, FL = fluorescence, PI = propidium iodide.