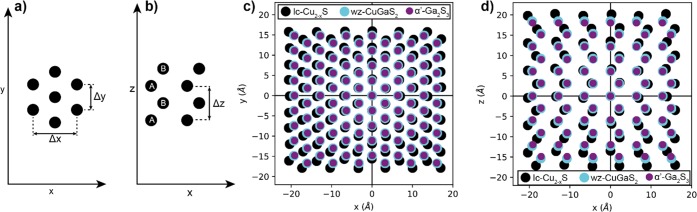
Figure 6.
(a,b) Hexagonal close-packed structure viewed from two different orientations: (a) characteristic arrangement into hexagonally constructed layers, defined here as the x,y-plane, and (b) characteristic ...ABAB... stacking of these hexagonal layers, defined here as the x,z-plane. (c,d) Anion positions of (black) low-chalcocite Cu2–xS, (cyan) wurtzite CuGaS2, and (purple) α′-Ga2S3 overlaid onto each other. (c) Hexagonal ordering in the x,y-plane and (d) ...ABAB... stacking in the x,z-plane. Δx, Δy, and Δz, denoted in (a,b), correspond to the lattice distances used to determine the lattice contractions mentioned in the main text. The x,y,z-directions correspond to the following crystallographic directions: (low-chalcocite Cu2–xS) [201],[010],[001]; (wurtzite CuGaS2) [11̅0],[110],[001]; (monoclinic α′-Ga2S3) [010],[100],[102]. Anion coordinates were obtained from the crystal structures of low-chalcocite Cu2–xS,34 wurtzite CuGaS2,44 and monoclinic α′-Ga2S3.46