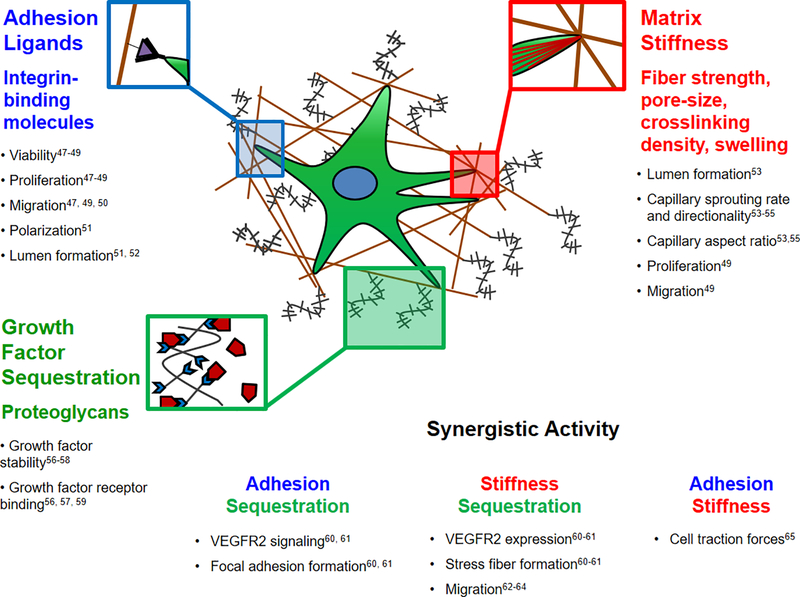
Figure 2.
Individual and synergistic effects of ECM properties on endothelial cell behaviors related to angiogenesis. Integrin-mediated cell adhesion influences endothelial cell viability, proliferation [47–49], migration [47, 49, 50], spatial polarization [51] and lumen formation [51, 52]. ECM modulus influences lumen formation [53], capillary sprouting rate and directionality [53–55], capillary aspect ratio [53, 55], proliferation, and migration [49]. Growth factor sequestration influences growth factor stability [56–58] and facilitates binding between growth factors and receptors [56, 57, 59]. Synergistically, integrin binding and growth factor sequestration influence VEGFR2 activity and focal adhesion assembly [60, 61]. Matrix modulus and growth factor sequestration influence VEGFR2 activity, cytoskeletal stress fiber formation and cell migration rate [62–64]. Finally, integrin binding and matrix modulus influence cell traction forces exerted and detected by endothelial cells [65].