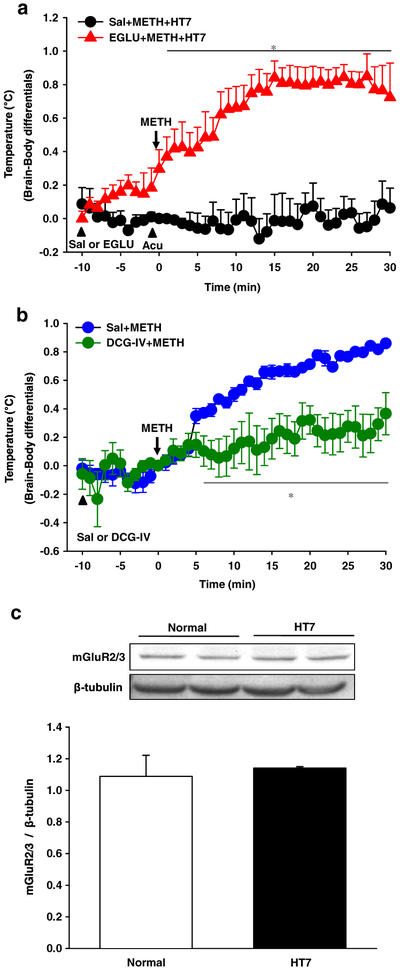
Figure 6.
Mediation of mGluR2/3 in inhibitory effect of acupuncture on methamphetamine (METH)-induced nucleus accumbens (NAc)–body temperature differentials. (a) Effect of an mGluR2/3 antagonist EGLU on acupuncture inhibition of NAc–body temperature differentials in METH-treated rats. *P < 0.05 versus Sal + METH + HT7. (b) Effect of an mGluR2/3 agonist DCG-IV on NAc–body temperature differentials in METH-treated rats. *P < 0.05 versus Sal + METH. Sal + METH + HT7, microinjection of saline (Sal) prior to acupuncture at HT7 in METH-treated rats; EGLU + METH + HT7, microinjection of EGLU prior to acupuncture at HT7 in METH-treated rats; Sal + METH, microinjection of Sal in METH-treated rats; DCG-IV + METH, microinjection of DCG-IV in METH-treated rats. (c) Western blot results for expression of mGluR2/3 in the NAc of normal rats or rats given acupuncture at HT7 (HT7). Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. N value is 5–7 per group for brain temperature and 4 per group for Western blot. Acu = acupuncture; DCG4 IV + METH = microinjection of DCG-IV in METH-treated rats; EGLU + METH + HT7 = microinjection of EGLU prior to acupuncture at HT7 in METH-treated rats; Sal + METH = microinjection of Sal in METH-treated rats; Sal + METH + HT7 = microinjection of Sal prior to acupuncture at HT7 in METH-treated rats