Figure 5.
ALS-Associated Mutations in ANXA11 Disrupt Its Interactions with Lysosomes
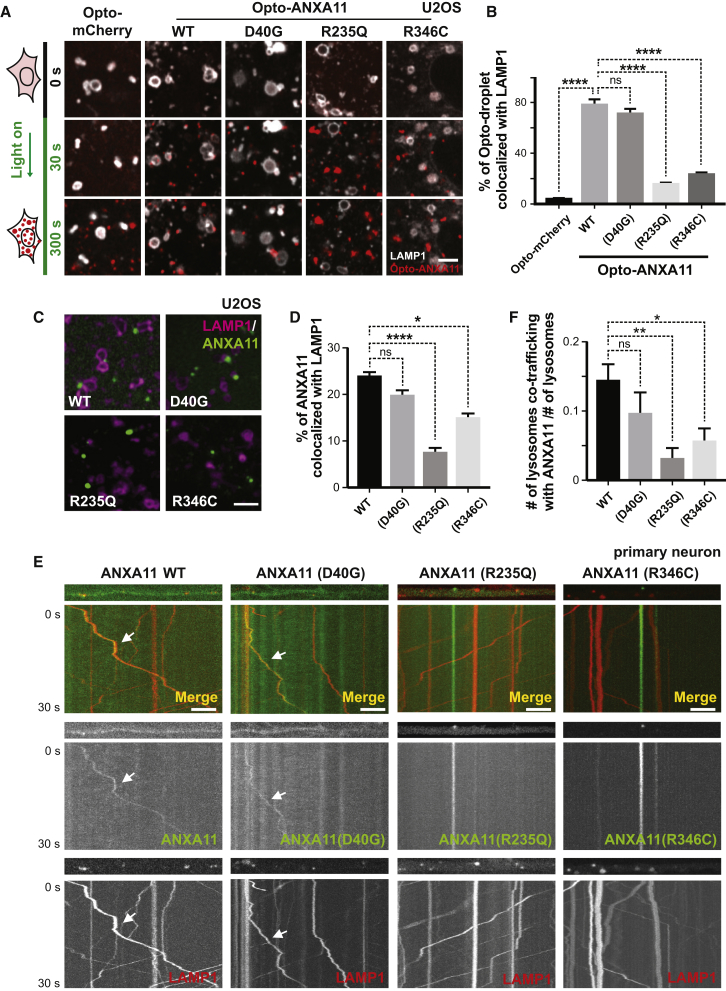
(A) Live cell imaging of Opto-mCherry, wild-type Opto-ANXA11, or mutant Opto-ANXA11 with LAMP1-HaloTag in U2OS cells before and after oligomerization induced by exposure to 488nm light. Scale bar: 2 μm. See also Figure S5A.
(B) Quantification of percentage of light-activated Opto-mcherry (CRY2olig-mCherry), wild-type Opto-ANXA11, or mutant Opto-ANXA11 clusters co-localizing with lysosomes at 300s post-488 nm light exposure from (A). n=26-30. One-way ANOVA, ns, not significant. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Error bars = SEM. See also Figure S5B.
(C) Extent of co-localization of wild-type or mutant ANXA11 with lysosomes. U2OS cells expressing LAMP1-HaloTag, wild-type ANXA11-mEmerald or mutant ANXA11-mEmerald were imaged 30 minutes after heat shock (43oC). Scale bar: 2 μm.
(D) Percentage of fluorescence associated with wild-type ANXA11 or mutant ANXA11 that co-localized with lysosomes from (C). n= 22-40. One-way ANOVA, ns, not significant. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. ∗p < 0.05. Error bars = SEM.
(E) Extent of co-trafficking of wild-type or mutant ANXA11 with lysosomes in axons. Axons of rat cortical neurons expressing LAMP1-HaloTag and wild-type or mutant ANXA11-mEmerald were imaged for 30 seconds. Kymographs show WT and p.D40G ANXA11 both co-traffic with lysosomes (see arrows) while p.R235Q and p.R346C each disrupt ANXA11 co-trafficking with lysosomes. Scale bar: 10 μm.
(F) Number of puncta containing WT or mutant ANXA11 that co-trafficked with lysosomes as a function of total lysosome number from (E). n= 21-30. One-way ANOVA, ns, not significant. ∗∗p < 0.01. ∗p < 0.05. Error bars = SEM.