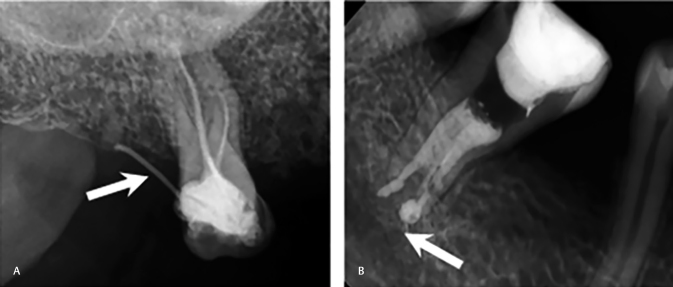
Fig. 3.
Periapical radiographs showing perforation of root canals communicating with the internal root canals to the external root surface, hence leading to blood contamination of the pulp space and potential infections; (A) bur perforation (arrow) of lateral wall of pulp chamber, leading to obturation materials and misdirecting into the gingival tissues, and (B) apical perforation (arrow) due to mechanical over instrumentation leading to extrusion of the obturation through the apical foramen.