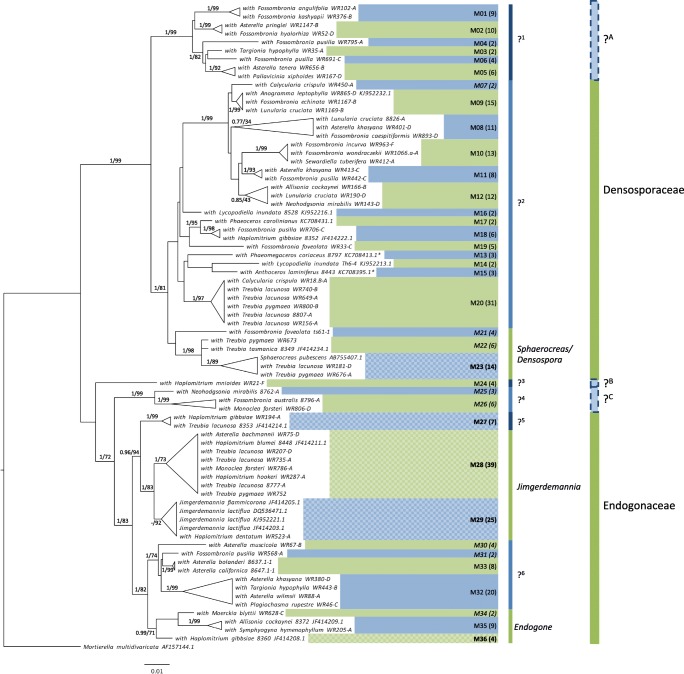
Fig. 1.
Diverse Mucoromycotina taxa colonize early-diverging plants. Maximum likelihood phylogeny of the Mucoromycotina that colonize liverworts and the results of species delimitation (epMT labels have been shortened to M) based on 18S DNA sequences. Support values are the result of both Bayesian inference and 1000 bootstrap replicates. Only support values for the main branches are provided—full support values and analysis settings are detailed in Fig. S1. A dash indicates Bayesian inference did not agree with maximum likelihood. Figures in brackets indicate the number of DNA sequences that belong to each epMT. The epMT in bold include sequences from Endogonales fruitbodies. Italicized epMT are specific to liverworts. Genus and family labels are based on Desirò et al. (2017). Question marks indicate putative new fungal genera (1–6) and families (A–C). Alternating blue and green are used to highlight different clades