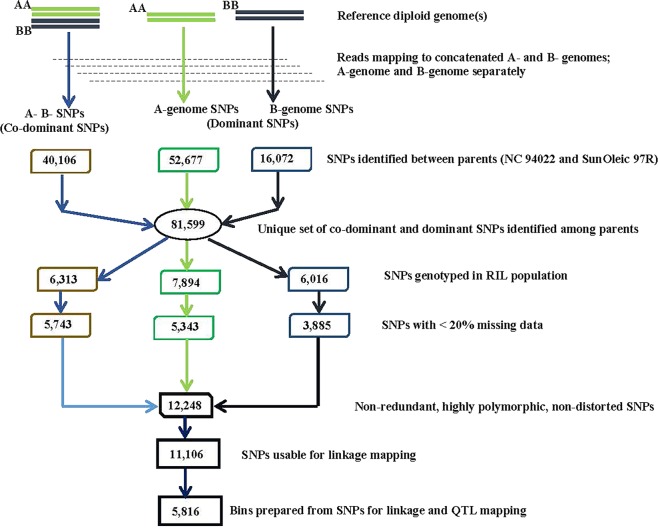
Figure 3.
Workflow of identification of polymorphic co-dominant and dominant SNPs used for developing bin maps in peanut using whole genome re-sequencing data. Fastq files were aligned to the concatenated (A- and B-genome together) genomes and individually to A- and B-genomes in order to identify co-dominant and dominant SNPs. A-genome represents Arachis duranensis and B genome represents Arachis ipaensis. A total of 81,599 non-redundant SNPs was identified between the two parents using the above-mentioned approach. Individually, the co-dominant and dominant SNPs identified were used for genotyping the RIL population to identify polymorphic SNPs (alleles) present in the population. After removing the SNPs with more than 20% missing data, a total of 12,248 unique set of SNPs were obtained. Excluding the SNPs showing segregation distortion, a final set of 11,106 SNPs were used for identification of 5,816 bins used in construction of linkage maps.