Figure 5.
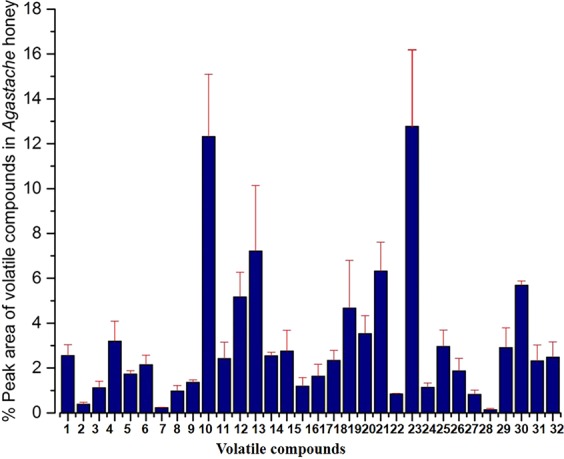
HS-SPME GC-MS volatile compounds identified in Agastache honey. Compounds were identified with GC-MS reference libraries (Adams, Wiley 7th and NIST 2.0) using a 70% similarity match cut-off value. The peak area in the total ion chromatograms was the basis of calculations of concentration of studied compounds. The error bar represents the mean of triplicate readings ± standard deviations (SD). 1-Benzaldehyde, 2-D-Limonene, 3-Benzeneacetaldehyde, 4-Nonanal, 5-Phenylethyl Alcohol, 6-1H-Pyrazole, 4,5-dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-4-isopropylidene-, 7-Cyclopentasiloxane, decamethyl-, 8-4,Ketoisophorone, 9-Octanoic acid, ethyl ester, 10-Estragole, 11-Decanal, 12-Benzaldehyde, 4-methoxy, 13-Nonanoic acid, ethyl ester, 14-Benzene, 1-methoxy-4-propyl, 15-Phenol, 2,3,5-trimethyl-, 16-Nonanoic acid, 17-Propanoic acid, 2-methyl-, 2-ethyl-3-hydroxyhexyl ester, 18-2H-Benzimidazol-2-one, 1,3-dihydro-5-methyl-, 19-β-Caryophyllene, 20-Benzoic acid, 4-methoxy-, ethyl ester, 21-2-Propenoic acid, 3-phenyl-, ethyl ester, 22-Y-cadinene, 23-Phenol, 2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl), 24-Benzoic acid, 3,5-dimethoxy-, methyl ester, 25-Dodecanoic acid, ethyl ester, 26-Y-Eudesmol, 27-Heptadecane, 28-Homosalate, 29-Nonadecane, 30-Hexadecanoic acid, ethyl ester, 31-Heneicosane, 32-9,12-Octadecadienoic acid (Z,Z). Data represent the mean of triplicate readings ± standard deviations (SD).
