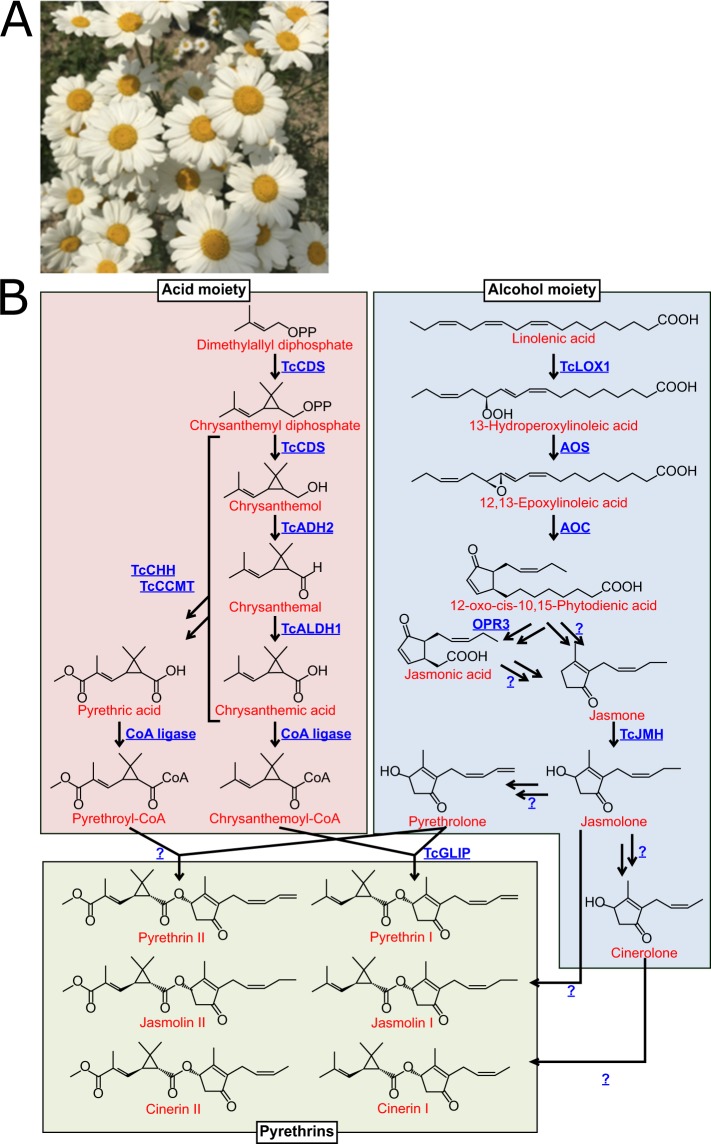
Figure 1.
Flower of T. cinerariifolium (A) and biosynthetic pathway of pyrethrins (B). Proposed biosynthetic pathway of pyrethrins. Chrysanthemic acid and pyrethric acid as acid moieties are synthesized from dimethylallyl diphosphates by T. cinerariifolium chrysanthemyl diphosphate synthase (TcCDS), T. cinerariifolium alcohol dehydrogenase 2 (TcADH2), T. cinerariifolium aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (TcALDH1), T. cinerariifolium chrysanthemol 10-hydroxylase (TcCHH), and T. cinerariifolium 10-carboxychrysanthemic acid 10-methyltransferase (TcCCMT). Pyrethrolone, jasmolone, and cinerolone as alcohol moieties are synthesized from linolenic acid by enzymes related to oxylipin pathway, including T. cinerariifolium jasmone hydroxylase (TcJMH), and unknown enzyme(s). Finally, chrysanthemoyl-CoA (the CoA-activated version of chrysanthemic acid) and pyrethrolone are esterified by T. cinerariifolium GDSL (Gly-Asp-Ser-Leu motif) lipase (TcGLIP) to produce pyrethrin I. Compounds and enzymes are indicated by red and blue text, respectively. Unidentified enzymes are indicated as question marks.