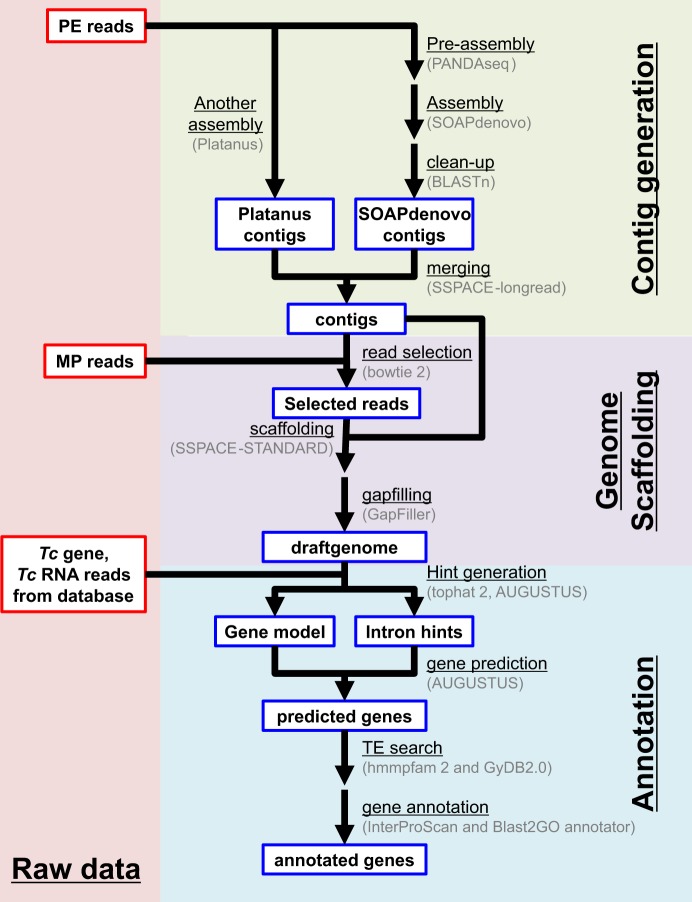
Figure 2.
Flowchart of genome assembly and gene prediction. The PE reads were subjected to contig assembly by a four-step process, including “pre-assembly” using PANDAseq, “contig assembly” using SOAPdenovo and Platanus, “clean-up” using BLASTN, and “merging with other assembly result” using SSPACE-longread. Then, the MP reads were subjected to scaffolding by a three-step process, including “read selection” using bowtie2, “scaffolding” using SSPACE-STANDARD, and “gapfilling” using GapFiller. These processes yielded the complete draft genome. The coding sequences in the draft genome then were annotated by a three-step process, including “gene prediction” using Augustus, “transposable elements (TEs) detection” using hmmpfam, and “protein superfamilies prediction” using InterProScan.