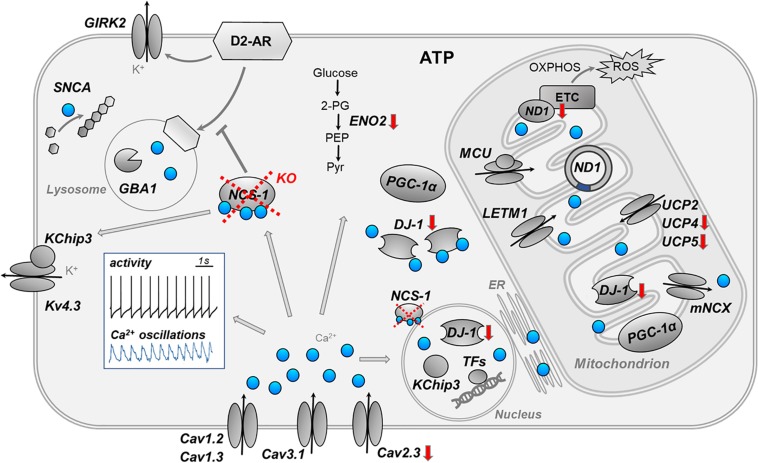
FIGURE 6.
Summary cartoon of detected gene expression changes in SN DA neuron from NCS-1 KO mice. The cartoon summarizes the main findings and conclusions of this study and illustrates the complex activity- and compartment-dependent roles of Ca2+ signaling in vulnerable SN DA neurons. The white insert-box illustrates the autonomous pacemaker activity (black trace) and the associated Ca2+ transients (blue trace) of SN DA neurons (perforated patch clamp and Calcium-imaging experiment, adapted from Liss and Striessnig (2019). Loss of NCS-1 is indicated by red cross, red arrows indicate transcriptional changes in NCS-1 KO mice. Ca2+ (blue dots) has a variety of different physiological and potentially detrimental functions in distinct compartments of SN DA neurons, like stimulating ATP synthesis enzymes, controlling gene expression, and triggering apoptosis. Ca2+ can indirectly inhibit electrical activity of SN DA neurons by stimulating NCS-1/D2-AR or Kv4.3/KChip3 activity. Similar as NCS-1, KChip3 (also known as DREAM or Calsenilin) is not only a β-subunit of voltage-gated Kv4.3 K+ channels, but it can also translocate from the plasma-membrane to the nucleus, where it controls Ca2+ dependent enzymes or gene expression. For further details, see text. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Cav, voltage-gated Ca2+ channel; DJ-1, protein deglycase; D2-AR, dopamine D2 autoreceptor; ENO2, neuron specific enolase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ETC, electron transfer chain; GBA1, glucocerebrosidase 1; GIRK2, G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying potassium channel; KChip3, Calsenilin (also known as DREAM); KO, knockout; Kv4.3, voltage-gated potassium channel subfamily D member; LETM1, leucine zipper EF-hand containing transmembrane protein 1; MCU, mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter (pore-forming subunit); mNCX, mitochondrial sodium-calcium exchanger; NCS-1, neuronal calcium sensor 1; ND1, NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase chain 1; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; Pyr, pyruvate; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SNCA, alpha-synuclein gene; TFs, transcription factors; UCP, uncoupling protein; 2-PG, 2-phosphoglycerate.